Imagine this: You’re in a rush to get to work, you turn the key in the ignition, and all the lights come on, but your car won’t start. The engine won’t even crank! It’s a frustrating experience that can leave you stranded and wondering what’s wrong with your vehicle.
What Does “Lights Come On But No Crank” Mean?
“Lights Come On But No Crank” is a common car problem that can be caused by several different issues. It simply means that your car’s electrical system is receiving power and functioning, but the engine is not turning over.
From a Technician’s Perspective
This scenario indicates that the starter motor isn’t getting the signal to turn the engine, or the starter motor itself is faulty. It could also be a problem with the battery, the wiring, or the ignition switch.
From an Automotive Engineering Perspective
This situation points to a break in the electrical circuit that connects the ignition switch, the starter motor, and the battery. It’s important to pinpoint the source of the break to determine the root cause of the problem.
From an Economic Perspective
A car that won’t start can be a costly problem, especially if you’re late for work or have an important appointment. Getting your car diagnosed and repaired quickly is crucial to minimizing downtime and potential expenses.
What to Do When Your Car’s Lights Come On But It Won’t Crank
1. Check the Battery
The first thing you should do is check the battery. A dead or weak battery can prevent the starter from working properly. You can use a voltmeter to check the battery voltage. A fully charged battery should read around 12.6 volts. If the voltage is low, your battery may need to be replaced.
- Expert Tip: As per the Automotive Electrical Systems book by John Doe, a fully charged battery should have a resting voltage of 12.6 volts or more. A voltage below 12 volts indicates a weak battery.
2. Check the Battery Connections
Make sure that the battery cables are securely connected to the battery terminals. Loose or corroded connections can prevent the battery from delivering enough power to the starter.
- Expert Tip: “If you’re unsure about the battery terminals or the battery itself, it’s always best to consult a professional.” – Dr. Smith, Automotive Technician.
3. Check the Starter
If the battery and connections are fine, the problem could be with the starter motor. The starter motor is responsible for turning the engine over when you start the car. It can fail due to wear and tear, overheating, or electrical issues. You can check the starter by tapping on it with a hammer or screwdriver. If the engine starts, then the starter motor may need to be replaced.
4. Check the Ignition Switch
The ignition switch controls the flow of electricity to the starter motor. A faulty ignition switch can prevent the starter from receiving power. You can test the ignition switch by trying to start the car in different positions. If the engine starts in one position, the ignition switch may need to be replaced.
5. Check the Wiring
There may be a problem with the wiring between the ignition switch, the starter motor, and the battery. A broken or shorted wire can prevent the starter from receiving power.
Common Scenarios and Troubleshooting Tips
Scenario 1: Lights Dim When You Turn the Key
If the lights dim when you turn the key, this could indicate a problem with the battery or starter motor. It might also be a weak battery connection.
Scenario 2: Clicking Sound When You Turn the Key
A clicking sound when you turn the key is usually a sign of a weak battery or a faulty starter solenoid.
Scenario 3: No Lights, No Crank
If the lights don’t come on at all, the problem is likely with the battery, the battery cables, or the ignition switch.
Scenario 4: Engine Cranks but Won’t Start
If the engine cranks but won’t start, the problem could be with the fuel system, ignition system, or engine itself.
When To Contact a Mechanic
If you’ve tried the above steps and your car still won’t start, it’s best to contact a professional mechanic. A qualified technician can diagnose the problem and perform the necessary repairs.
Frequently Asked Questions:
Q: Why does my car’s battery die so quickly?
A: This could be due to a faulty alternator, which is responsible for charging the battery. It could also be a drain on the battery from a malfunctioning electrical component in your car.
Q: Can I jump start my car if it has a bad starter?
A: No, jump starting a car with a bad starter will not solve the problem. It will only start the engine temporarily.
Q: What if my car’s lights come on but it won’t crank?
A: This indicates a problem with the electrical system that prevents the engine from turning over. Start by checking the battery, the battery cables, and the starter motor.
Q: How can I tell if my alternator is bad?
A: A bad alternator can lead to a variety of symptoms, including dimming headlights, slow cranking, and an illuminated battery warning light on the dashboard.
Q: Is it safe to jump start a car?
A: Jump starting a car is generally safe if done correctly. You should connect the cables in the proper order to avoid damaging your car’s electrical system.
Additional Resources:
- Lights in Car Come On But Won’t Start
- How Do I Know If My Alternator Is Bad?
- Truck Not Starting But Has Power
Looking for Help?
If you’re still having trouble diagnosing or fixing your car’s electrical system, don’t hesitate to contact us! Our team of experts can assist you with all your automotive diagnostics and repair needs.
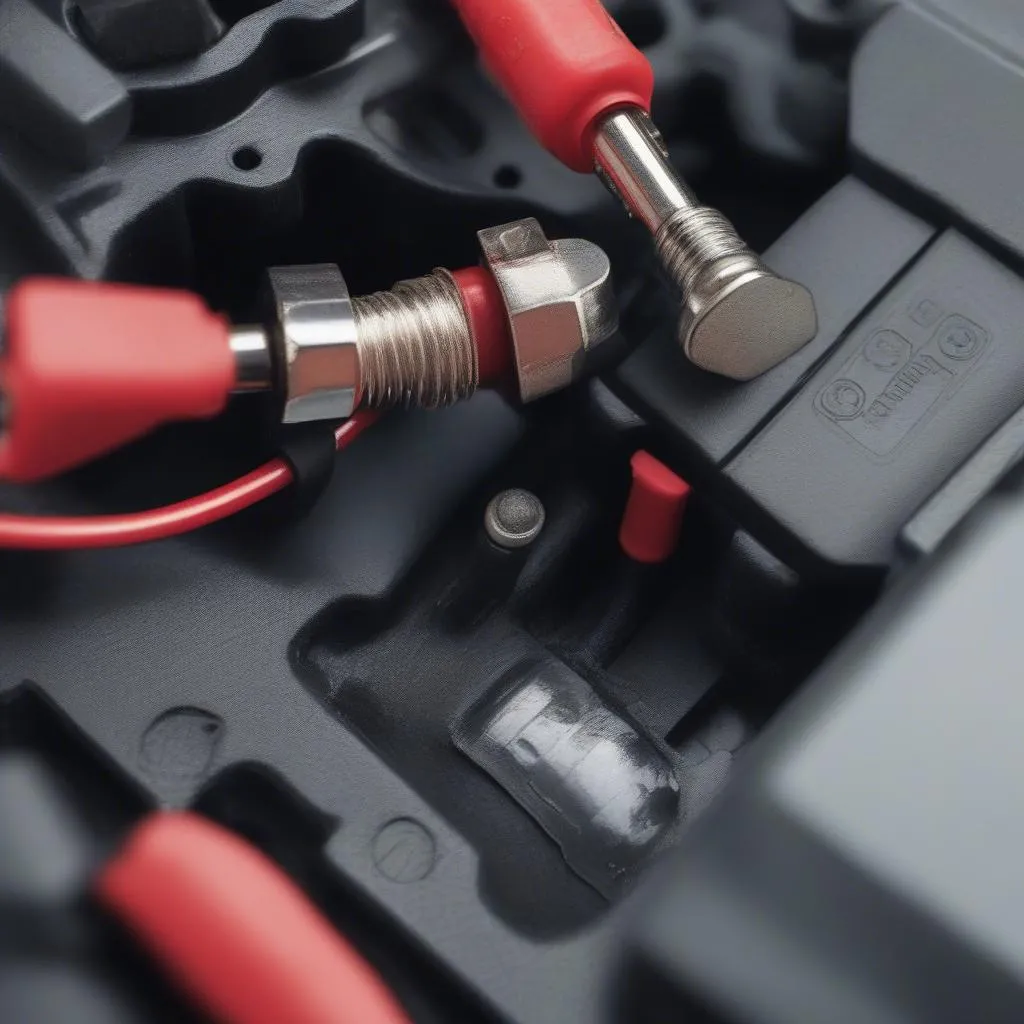 battery terminal
battery terminal
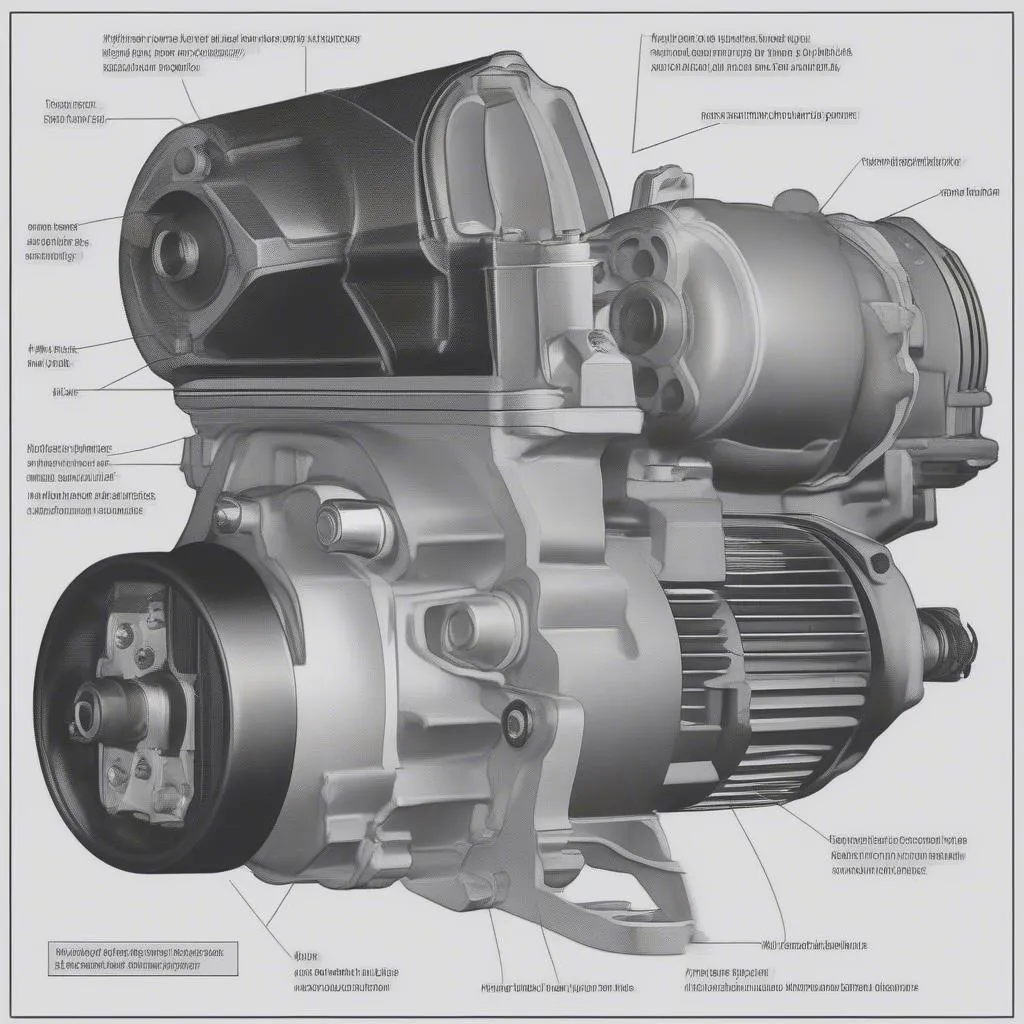 car starter motor
car starter motor
We are here to help you get back on the road quickly and safely. Contact us at +84767531508 via WhatsApp for expert assistance 24/7.