Imagine this: You’re driving your BMW 3 Series down a busy road in Los Angeles, enjoying the smooth ride and powerful engine. Suddenly, you feel a wave of weakness wash over you, your vision blurs, and you start to sweat. You’re experiencing the tell-tale signs of hypoglycemia, a condition where your blood sugar levels drop dangerously low. This experience can be scary, but don’t worry, with proper self-care, you can manage hypoglycemia and stay in control.
Understanding Hypoglycemia and Its Impact
Hypoglycemia, also known as low blood sugar, is a common condition, especially among people with diabetes. It can also occur in individuals with other medical conditions or those taking certain medications.
What Does Hypoglycemia Feel Like?
Hypoglycemia can manifest in various ways, ranging from mild to severe. Some common symptoms include:
- Feeling shaky or trembling: This happens because your body is trying to get more glucose into your bloodstream.
- Feeling lightheaded or dizzy: Low blood sugar can affect your brain function, leading to dizziness.
- Experiencing confusion or difficulty concentrating: A lack of glucose can impair cognitive function.
- Breaking out in a cold sweat: Your body’s response to low blood sugar.
- Feeling irritable or anxious: Low blood sugar can trigger mood swings.
Self-Care Strategies for Hypoglycemia
The good news is that you can effectively manage hypoglycemia with proper self-care. Here’s a comprehensive guide:
1. Know Your Triggers:
- Regular Blood Sugar Monitoring: Regularly monitoring your blood sugar levels with a glucose meter can help identify patterns and potential triggers.
- Diet and Exercise: Certain foods can cause rapid fluctuations in blood sugar levels. Pay attention to your diet, including the timing and types of food you consume. Regular exercise can also affect blood sugar levels, so it’s essential to be mindful of your routine.
2. Carry Glucose Tablets or Juice:
- Quick Fixes: It’s crucial to carry a quick-acting source of glucose, such as glucose tablets or juice, for immediate relief when you experience hypoglycemia.
3. Seek Medical Advice:
- Understanding Your Condition: Consult with your doctor or a healthcare professional to discuss your individual hypoglycemia triggers and develop a personalized management plan.
- Medication Review: If you are on any medications, discuss with your doctor if they may be contributing to hypoglycemia.
Hypoglycemia: A Case Study
John, a 45-year-old mechanic in Chicago, had been struggling with hypoglycemia for a few years. He worked long hours at a local Ford dealership, and his demanding schedule often led to him skipping meals or eating unhealthy snacks on the go. John started experiencing frequent episodes of hypoglycemia, causing him to feel fatigued, dizzy, and even confused.
Realizing the severity of his condition, John sought help from a diabetes specialist. The specialist advised John to manage his diet, exercise regularly, and carry glucose tablets with him at all times. He also recommended John to check his blood sugar levels regularly to identify his personal triggers.
Following the doctor’s recommendations, John was able to significantly reduce his hypoglycemia episodes. He learned to prioritize his meals, snack regularly, and monitor his blood sugar levels throughout the day. This experience taught John the importance of self-care and the power of knowledge in managing his condition.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
1. What is the difference between hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia?
Hypoglycemia refers to low blood sugar levels, while hyperglycemia refers to high blood sugar levels. Both conditions are problematic and require different management strategies.
2. Can hypoglycemia be dangerous?
Yes, severe hypoglycemia can be dangerous. It can lead to seizures, loss of consciousness, and even coma if left untreated.
3. What are the long-term effects of hypoglycemia?
Frequent episodes of hypoglycemia can have long-term effects on your brain, nervous system, and overall health.
4. How can I prevent hypoglycemia?
Preventing hypoglycemia involves regular blood sugar monitoring, a healthy diet, regular exercise, and medication management if applicable.
Conclusion
Living with hypoglycemia can be challenging, but it’s manageable with the right knowledge and self-care strategies. By being aware of your triggers, having access to quick-acting glucose sources, and consulting with healthcare professionals, you can effectively manage your condition and lead a healthy, fulfilling life.
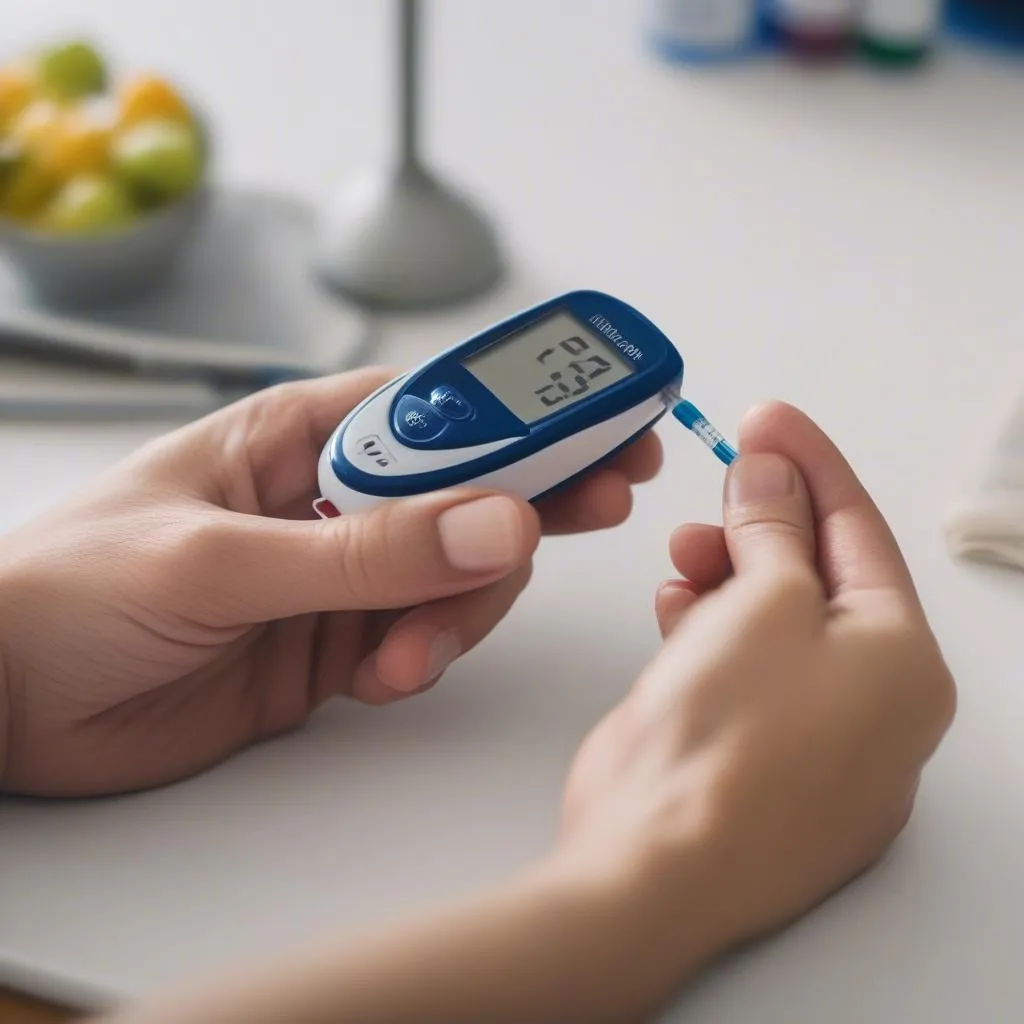 Using a glucose meter to monitor blood sugar levels
Using a glucose meter to monitor blood sugar levels
Remember, you are not alone. If you are experiencing hypoglycemia, seek professional guidance from a healthcare provider. We are here to support you on your journey to managing your condition effectively.
Need help with setting up your diagnostic tools? Contact us on WhatsApp at +84767531508. Our team of experts is available 24/7 to assist you.