An OBD scanner (OBD2 scanner) is a device that allows you to communicate with your car’s computer system and retrieve diagnostic information. It’s a valuable tool for DIY car maintenance, troubleshooting, and understanding your vehicle’s health. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the process of using an OBD scanner, from connecting it to interpreting the data.
Connecting Your OBD Scanner
Before you start, locate your vehicle’s OBD-II port. It’s usually found under the dashboard on the driver’s side. Once you’ve found it, follow these steps:
- Turn off your vehicle’s ignition.
- Plug the OBD scanner into the OBD-II port. Ensure a secure connection.
- Turn the ignition to the “on” position. This powers up the scanner but doesn’t start the engine.
- Wait for the scanner to initialize. This may take a few seconds.
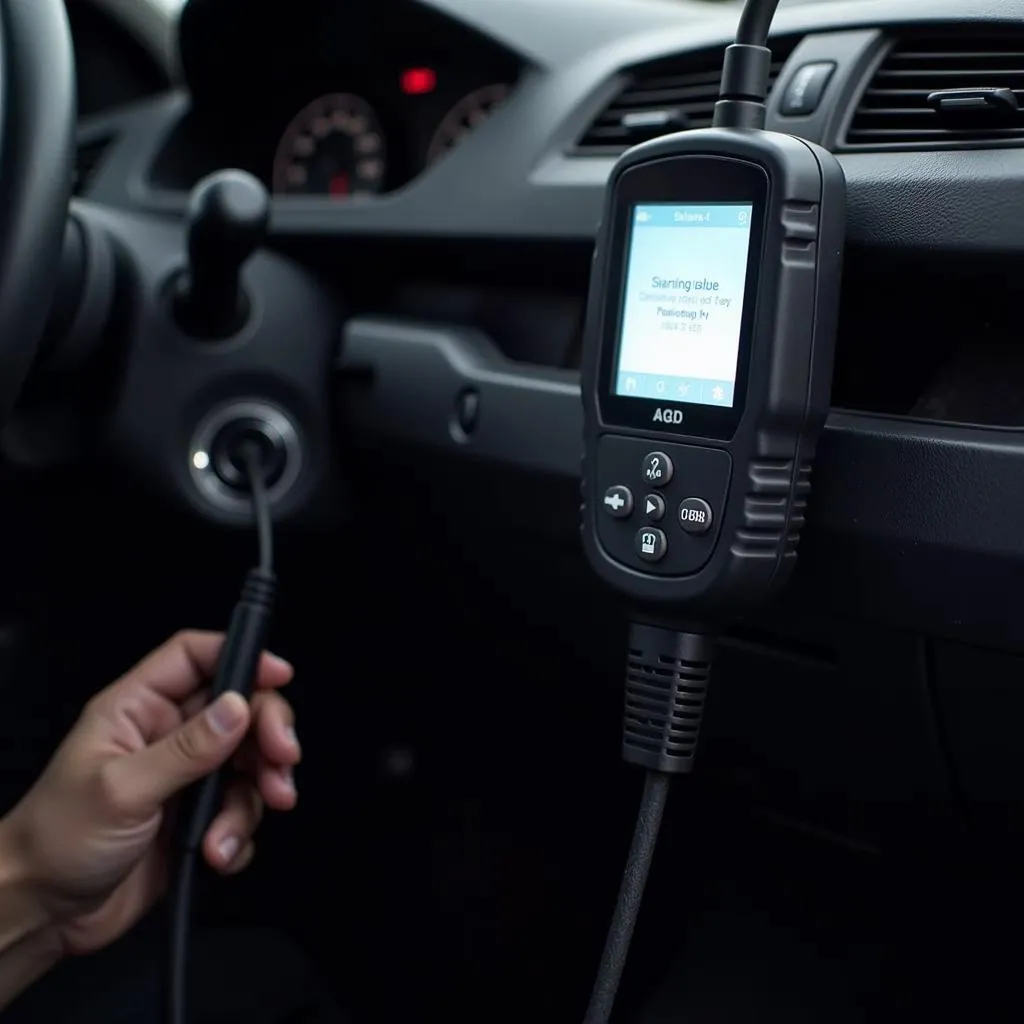 OBD Scanner Connected to Car
OBD Scanner Connected to Car
Reading and Understanding OBD-II Codes
Once the scanner is connected, it will typically display a list of diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs). These codes are standardized, meaning they have the same meaning across different makes and models. Each code is a five-digit alphanumeric sequence that indicates a specific problem area. Here’s how to decipher them:
- The first digit indicates the system:
- P: Powertrain (engine, transmission, emissions)
- B: Body (airbags, power windows, central locking)
- C: Chassis (ABS, traction control, steering)
- U: Network & Communication (CAN bus, modules)
- The second digit indicates the type of code:
- 0: Generic (SAE standard)
- 1: Manufacturer-specific
- The last three digits indicate the specific problem.
 OBD Scanner Displaying Trouble Code
OBD Scanner Displaying Trouble Code
For example, the code P0420 indicates a generic powertrain issue related to the catalytic converter system. To understand the specific meaning of a code, refer to your vehicle’s service manual or an online database.
Going Beyond Basic Code Reading
Most OBD scanners can do more than just read codes. They offer a range of features that can help you diagnose and fix problems:
- Live data: View real-time sensor data, such as engine RPM, coolant temperature, and oxygen sensor readings. This can be invaluable for pinpointing issues.
- Freeze frame data: Captures a snapshot of sensor data at the moment a trouble code was stored. This helps recreate the conditions that led to the problem.
- Clearing codes: After repairing a problem, you can use the scanner to clear the stored trouble code. This ensures the check engine light turns off and prevents future misdiagnoses.
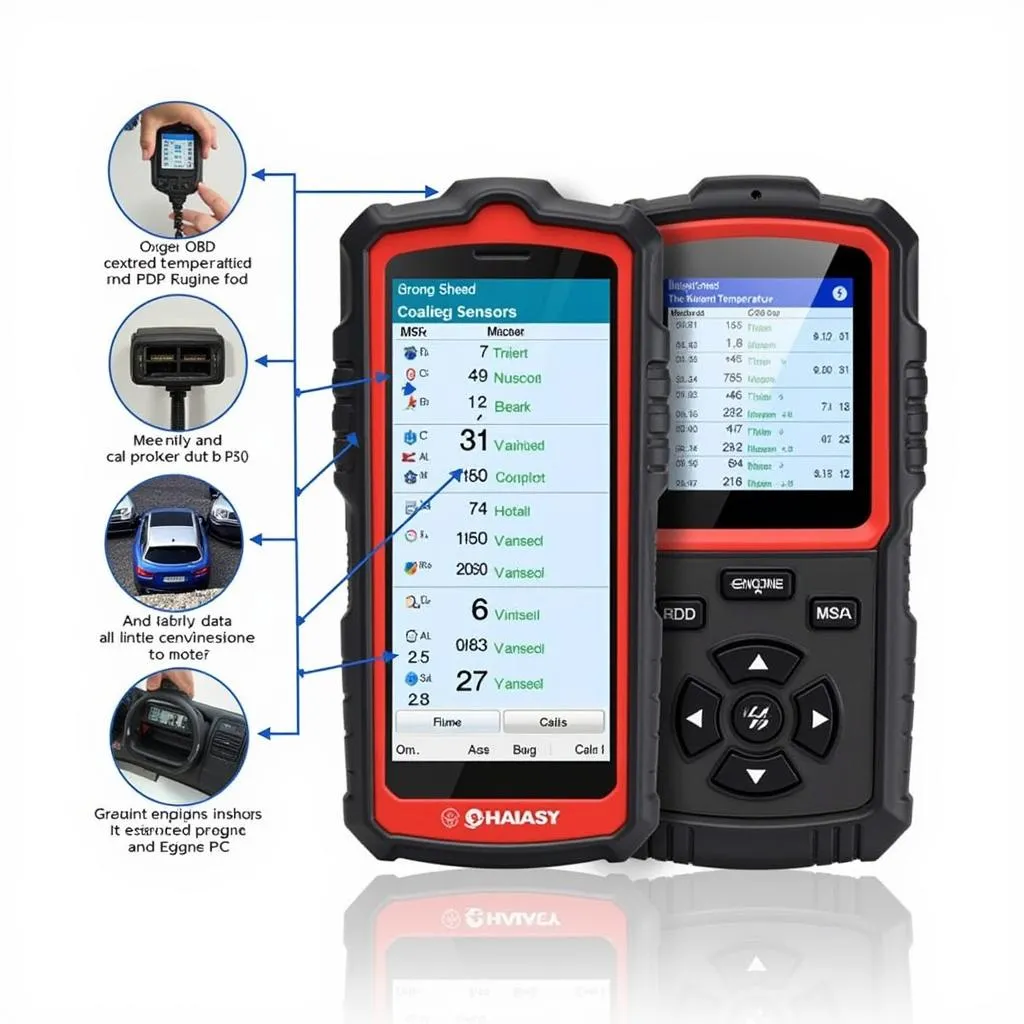 OBD Scanner Showing Live Data
OBD Scanner Showing Live Data
Choosing the Right OBD Scanner
OBD scanners come in a wide range of prices and features. Here’s a quick guide to help you choose the right one:
- Basic code readers: These are the most affordable options and are good for reading and clearing codes.
- Mid-range scanners: Offer additional features like live data, freeze frame data, and the ability to graph data over time.
- Professional-grade scanners: Provide advanced functionality, including bidirectional control (the ability to control vehicle systems), module programming, and access to manufacturer-specific codes.
Consider your needs and budget when making your choice. If you’re a DIYer, a mid-range scanner is a good investment. If you’re a professional mechanic, you’ll need a professional-grade scanner.
Conclusion
Knowing how to use an OBD scanner is a valuable skill for any car owner. It empowers you to diagnose problems, save money on repairs, and gain a deeper understanding of your vehicle’s health. Remember to consult your vehicle’s service manual or a trusted mechanic if you encounter any complex issues.
FAQs
Q: Can I use any OBD scanner on my car?
A: Most cars manufactured after 1996 in the US (and 2001 in Europe) are OBD-II compliant, meaning they use the same standard connector and communication protocol.
Q: What does it mean if my check engine light is flashing?
A: A flashing check engine light usually indicates a serious problem that requires immediate attention.
Q: Can I fix the problem myself after diagnosing it with an OBD scanner?
A: While an OBD scanner can help you identify the problem, it doesn’t necessarily mean you can fix it yourself. Some repairs require specialized tools and knowledge.
Q: How often should I use my OBD scanner?
A: It’s a good idea to scan your car for codes periodically, even if there are no warning lights illuminated. This can help you catch problems early on before they become more serious.
Q: Where can I find more information about OBD-II codes?
A: Numerous online resources provide detailed information about OBD-II codes, including their descriptions and possible causes.
If you’re experiencing issues with your battery or alternator, check out our articles on [bad battery or alternator], [starter vs alternator problems], [alternator vs battery], [starter or alternator], or [dead battery or starter] for more information and troubleshooting tips.
For any assistance with your car diagnostic needs, please feel free to reach out to us. Our dedicated team is available 24/7 to provide expert advice and support. You can contact us via WhatsApp at +1(641)206-8880, email us at [email protected], or visit us at 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States.