Imagine this: you’re driving down the Pacific Coast Highway in your classic 1967 Ford Mustang, the California sun warming your face. Suddenly, your check engine light pops on. You pull over, a pit forming in your stomach. Is it something serious? Expensive?
Understanding your car’s sensors, especially the oxygen sensor (O2 sensor), and knowing how to read them on a scan tool, can be incredibly empowering. It can save you unnecessary trips to the mechanic and help you diagnose issues before they escalate.
Deciphering the O2 Sensor: What It Tells You
From a mechanic’s perspective, the O2 sensor is like the canary in the coal mine for your engine. It measures the oxygen content in your car’s exhaust, providing crucial data about your engine’s air-fuel mixture. This information is vital for fuel efficiency, engine performance, and reducing harmful emissions.
From a technical standpoint, the O2 sensor generates a voltage signal that fluctuates based on the oxygen level. A rich air-fuel mixture (too much fuel) results in a high voltage signal, while a lean mixture (too much air) produces a low voltage.
“Understanding these readings is like learning a new language about your car,” says fictional mechanic and author, James “Sparkplug” O’Reilly, in his book “Engine Whispering.” “It allows you to have a deeper conversation with your vehicle and anticipate its needs.”
 Reading O2 Sensor Values on Scan Tool
Reading O2 Sensor Values on Scan Tool
Decoding the Data: How to Use a Scan Tool
Now, let’s talk about how to use a scan tool to read your O2 sensors:
- Locate the OBD-II port: This is usually found under the driver’s side dashboard.
- Connect your scan tool: Turn on your ignition but don’t start the engine.
- Access the live data stream: This will display various sensor readings, including your O2 sensors.
You should see readings for at least one upstream and one downstream O2 sensor. The upstream sensor is located before the catalytic converter and primarily monitors the air-fuel mixture. The downstream sensor, positioned after the converter, checks its efficiency.
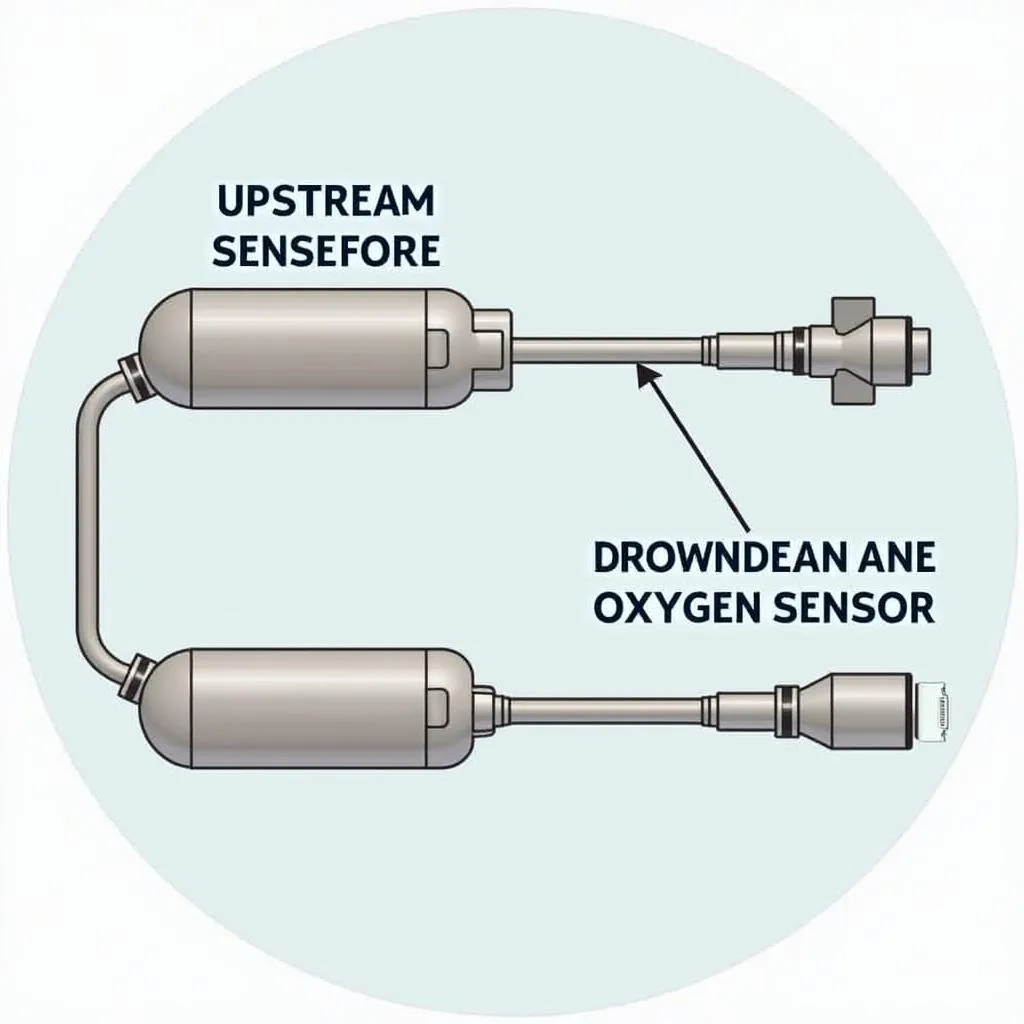 Upstream and Downstream O2 Sensor Locations in a Car
Upstream and Downstream O2 Sensor Locations in a Car
What to Look For: Interpreting the Readings
- Fluctuating Voltage: A healthy O2 sensor should rapidly switch between a high and low voltage, indicating a constantly adjusting air-fuel mixture.
- Slow or Static Readings: This can point to a faulty O2 sensor, wiring issues, or problems with the engine’s fuel delivery system.
- High Voltage: A consistently high voltage from the upstream sensor may suggest a rich air-fuel mixture, potentially caused by a clogged air filter, malfunctioning fuel injector, or a faulty Mass Air Flow (MAF) sensor.
- Low Voltage: A consistently low voltage reading from the upstream sensor could indicate a lean air-fuel mixture, possibly due to a vacuum leak, a faulty fuel pump, or a restricted fuel filter.
Common Questions About Reading O2 Sensors
What should the O2 sensor readings be at idle?
At idle, the upstream O2 sensor voltage should fluctuate between 0.1 volts (lean) and 0.9 volts (rich). The downstream sensor, on the other hand, should remain relatively steady, indicating the catalytic converter is working efficiently.
Can I drive with a bad O2 sensor?
While you might be able to drive for a short distance with a bad O2 sensor, it’s not recommended. A faulty O2 sensor can lead to decreased fuel efficiency, increased emissions, and potentially damage your catalytic converter, which can be a costly repair.
Troubleshooting O2 Sensor Problems: Taking Action
If you suspect a problem with your O2 sensor, here’s what you can do:
- Visually inspect the sensor: Look for any physical damage, such as burns, cracks, or loose wiring.
- Check for engine codes: Use your scan tool to read any stored Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) related to the O2 sensor.
- Test the sensor voltage: With the engine running, monitor the sensor voltage on your scan tool.
- Consult a professional: If you’re unsure about any aspect of diagnosing or replacing an O2 sensor, it’s always best to consult a qualified mechanic.
Exploring Further: Related Questions
- How often should O2 sensors be replaced?
- Can a bad O2 sensor cause my car to fail emissions?
- What are the symptoms of a bad catalytic converter?
For a more in-depth look at the OXGORD MS300 OBD2 scan tool, a powerful and affordable option for DIY car maintenance, check out our reviews:
Remember, knowledge is power when it comes to car maintenance. Understanding how to read O2 sensors on a scan tool can save you time, money, and unnecessary headaches down the road.
Need Help? We’re Just a Message Away!
If you need assistance setting up or using diagnostic tools, our team of auto repair experts is available 24/7. Contact us on Whatsapp: +84767531508. We’re here to help you keep your car running smoothly.


