Imagine this: You’re driving your car down the highway, enjoying the open road, when suddenly your engine starts sputtering and losing power. You pull over, check under the hood, and find nothing obvious amiss. But deep down, you know something is wrong.
What if I told you this could be a sign of a faulty oxygen sensor?
Today, we’re diving into the world of oxygen sensors and how to read them using a scan tool. This is a critical skill for any car owner or mechanic, as it can help identify a range of issues with your engine’s efficiency and performance.
The Importance of Understanding O2 Sensor Readings
The oxygen sensor is a vital component of your car’s exhaust system. It monitors the amount of oxygen in the exhaust gases and sends this information to the engine control unit (ECU). This data is crucial for the ECU to adjust the air-fuel mixture, ensuring optimal combustion and minimizing emissions.
Why is understanding O2 sensor readings so important?
- Early Warning System: A faulty oxygen sensor can lead to various engine problems, including poor fuel economy, decreased power, and even engine damage. Being able to read O2 sensor data can help you identify these issues early on, before they escalate.
- Fuel Efficiency and Emissions: Properly functioning oxygen sensors are essential for maintaining fuel efficiency and reducing harmful emissions.
- Diagnosis and Troubleshooting: A scan tool reading can provide invaluable insights into the health of your engine and its performance.
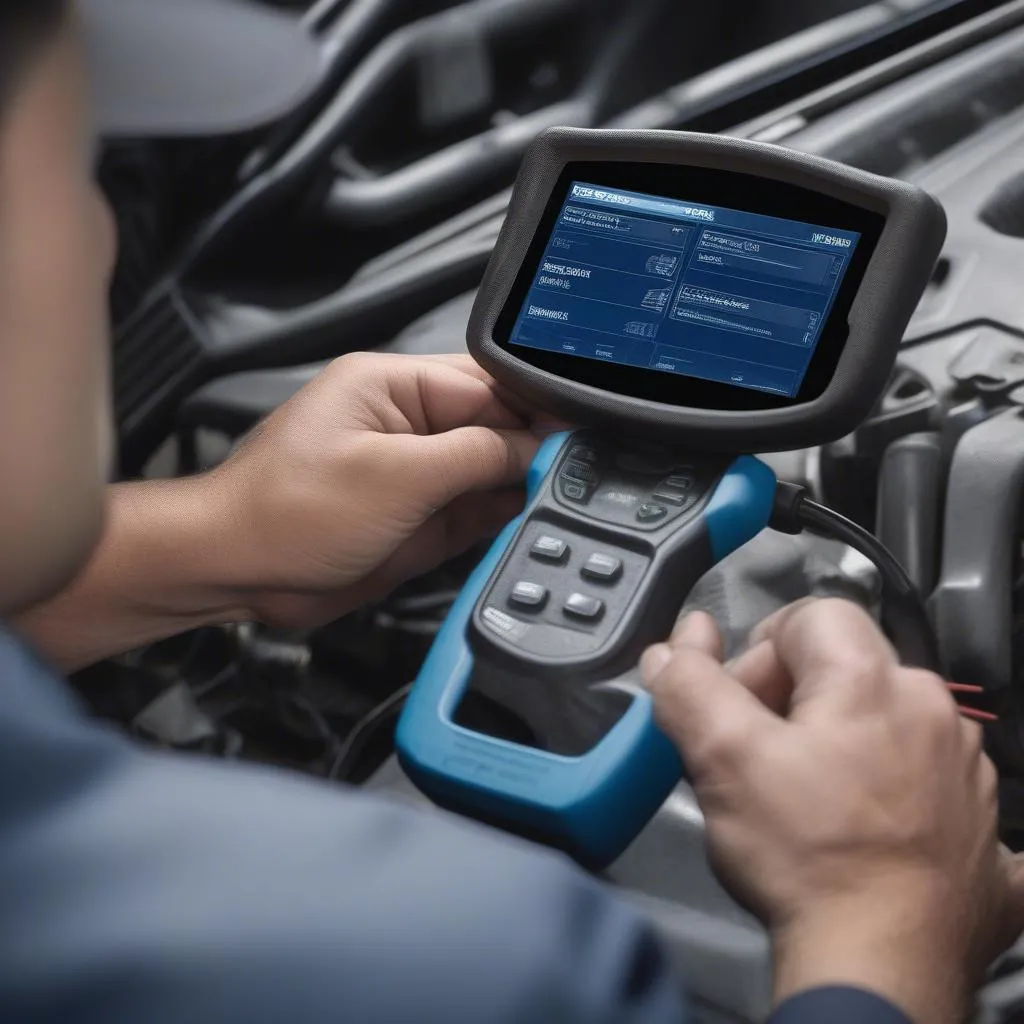
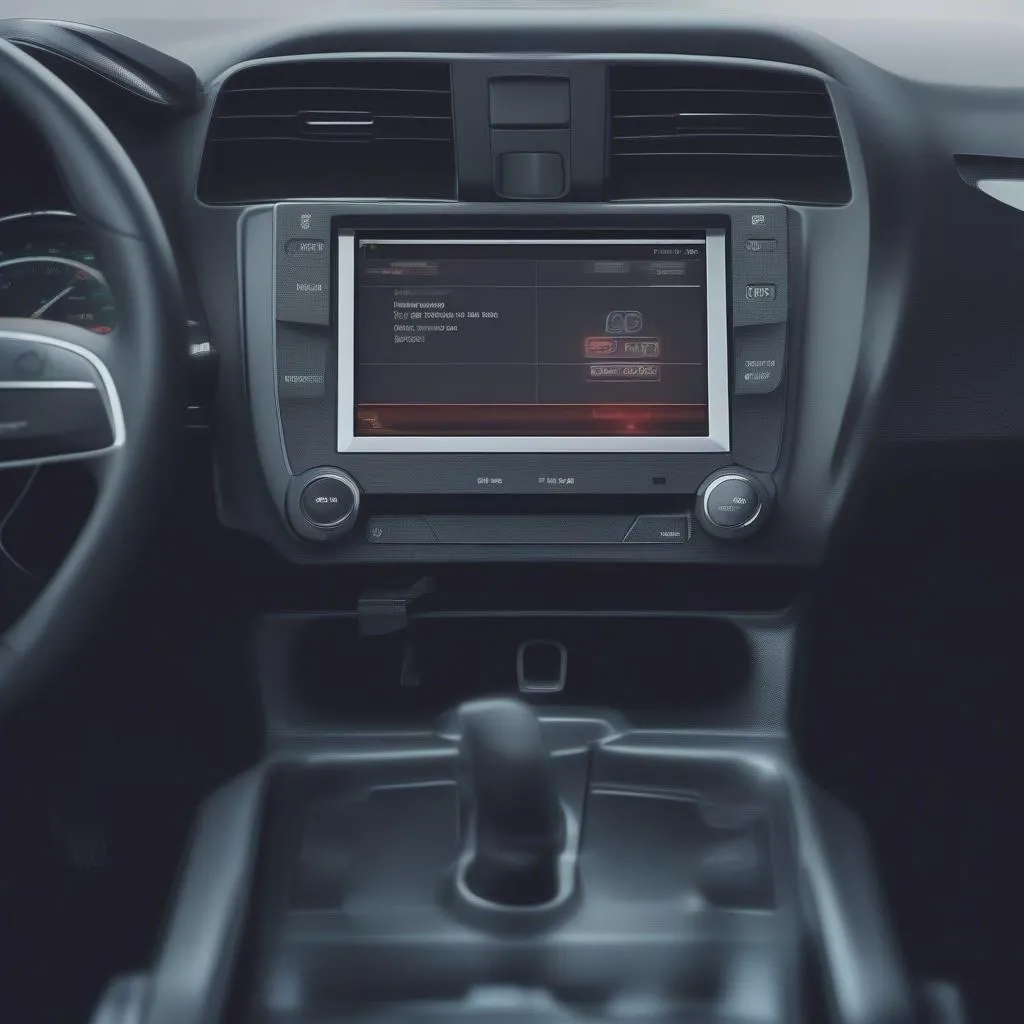
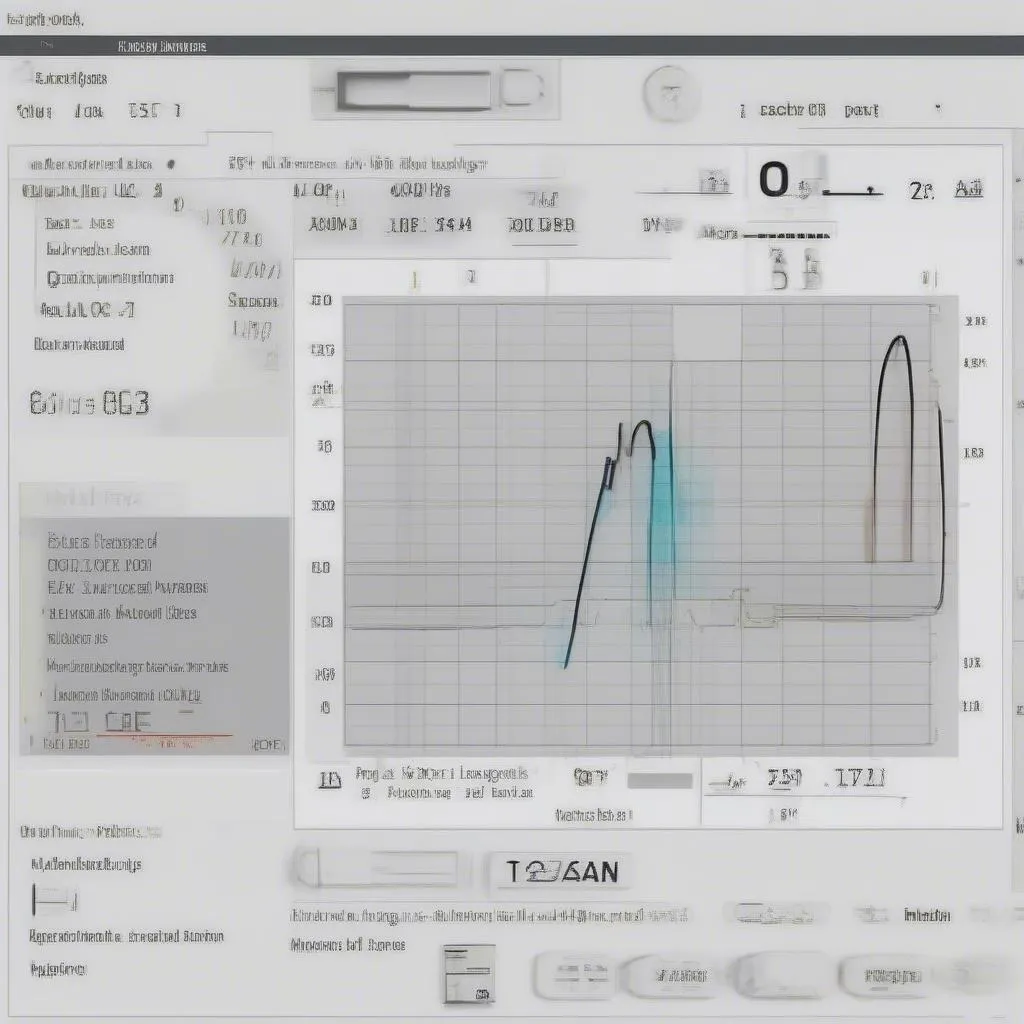 Oxygen sensor reading on a scan tool
Oxygen sensor reading on a scan tool
How to Read O2 Sensor Data with a Scan Tool
What You’ll Need:
- A Scan Tool: You’ll need a scan tool capable of reading data from your car’s OBD-II port. A scan tool can range from basic models that read codes to advanced ones that can display live data streams, including O2 sensor readings.
- OBD-II Adapter: For some older vehicles, you might need an OBD-II adapter to connect the scan tool to your car.
Steps to Read O2 Sensor Data:
-
Connect the Scan Tool: Connect your scan tool to your car’s OBD-II port, typically located under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
-
Select “Live Data”: Navigate to the “Live Data” or “Data Stream” section of your scan tool.
-
Find O2 Sensor Readings: Look for the O2 sensor readings in the data stream. Most scan tools will list the readings for each O2 sensor in your exhaust system, typically labeled as “O2 Sensor 1 Bank 1,” “O2 Sensor 2 Bank 1,” etc.
-
Interpret the Readings: O2 sensor readings are typically displayed in millivolts (mV). A healthy O2 sensor reading should oscillate between approximately 0.1V to 0.9V while the engine is running.
Important Notes:
- Sensor Location: Most cars have an upstream sensor (before the catalytic converter) and a downstream sensor (after the catalytic converter).
- Voltage Fluctuations: The voltage readings should fluctuate rapidly, indicating that the sensor is actively measuring the oxygen levels in the exhaust.
- Frozen Readings: A frozen or static reading (not fluctuating) may indicate a faulty sensor.
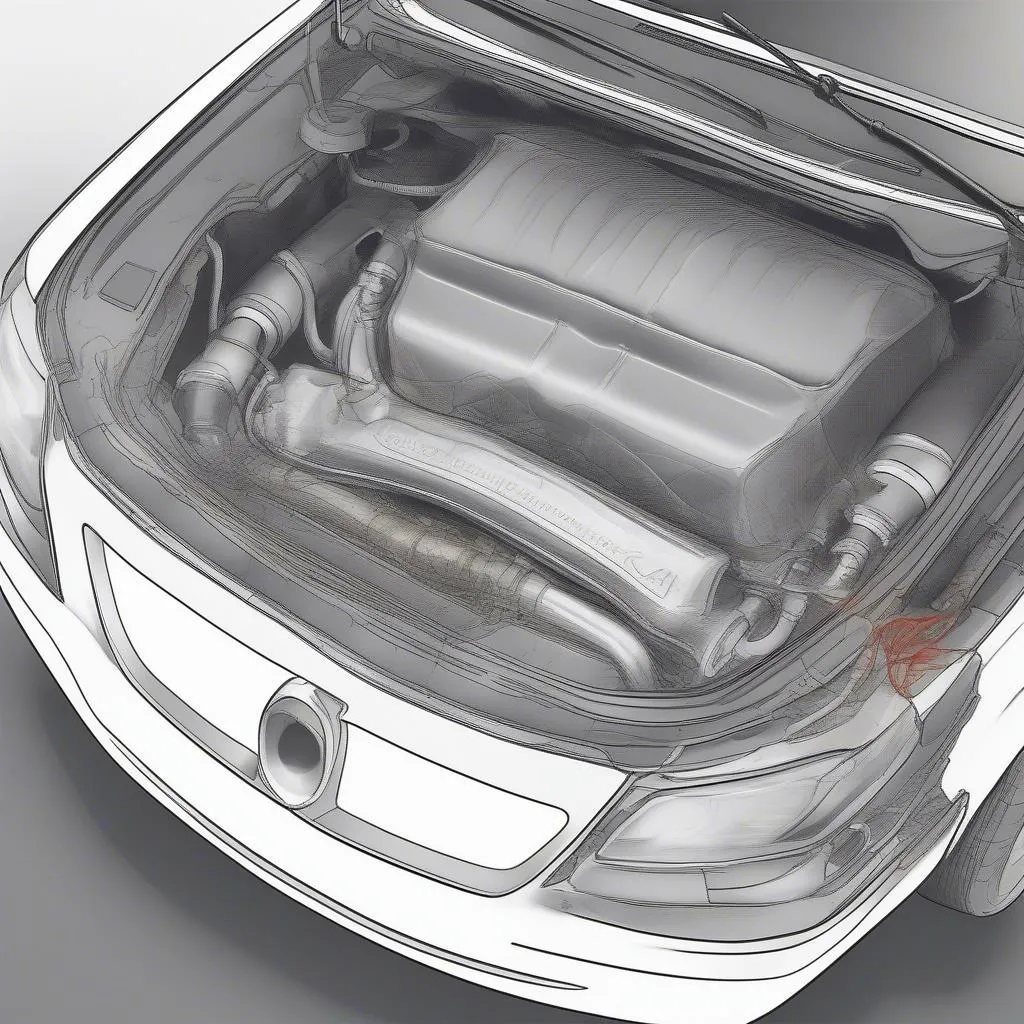 Oxygen sensor location on a car
Oxygen sensor location on a car
What to Look for in O2 Sensor Readings
Common O2 Sensor Issues:
- High or Low Readings: O2 sensor readings that consistently stay high or low can point to a faulty sensor.
- Slow Response Time: If the O2 sensor reading is slow to respond to changes in engine load or RPM, it could be malfunctioning.
- No Readings: A complete lack of O2 sensor readings may indicate a wiring issue, a broken sensor, or a problem with the ECU.
How to Diagnose O2 Sensor Problems:
- Visual Inspection: Inspect the O2 sensor for any signs of damage, corrosion, or leaks.
- Voltage Testing: Use a multimeter to test the voltage output of the O2 sensor.
- Data Stream Analysis: Use a scan tool to examine the O2 sensor readings and look for any unusual patterns or inconsistencies.
- Replace the Sensor: If all else fails, replacing the O2 sensor may be necessary.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What are the symptoms of a bad O2 sensor?
A: A bad O2 sensor can cause a variety of symptoms, including:
- Reduced fuel efficiency
- Engine misfire
- Increased emissions
- Check engine light (CEL) illuminated
Q: How often should I replace my O2 sensors?
A: O2 sensors typically last between 50,000 and 100,000 miles. However, factors like driving conditions and engine wear can impact their lifespan.
Q: Can I replace an O2 sensor myself?
A: Replacing an O2 sensor is a relatively straightforward task, but it’s important to consult your owner’s manual or a professional mechanic for guidance.
Q: How do I know if my scan tool can read O2 sensor data?
A: Most modern scan tools can read O2 sensor data. However, it’s always best to consult your scan tool’s manual or documentation to ensure compatibility with your vehicle.
Next Steps:
Understanding how to read O2 sensor data with a scan tool can empower you to diagnose and troubleshoot engine problems efficiently.
If you need further guidance or support, consider consulting our https://diagxcar.com/what-should-the-o2-senseor-mv-read-on-scan-tool/ article or reaching out to our team of experts.
We can assist you with:
- Selecting the right scan tool for your needs.
- Troubleshooting O2 sensor issues.
- Providing expert guidance on diagnosing and resolving engine problems.
Contact us today at +84767531508 via WhatsApp for 24/7 support and get your car running smoothly again!
Let’s keep your car running smoothly and efficiently!