Have you ever wondered how your car knows when to adjust its fuel mixture for optimal performance? The answer lies in the humble oxygen sensor, a vital component that monitors the exhaust gases and sends this information to the engine control unit (ECU). But what if you suspect your O2 sensor is malfunctioning? How do you check it with a scan tool?
Understanding the Importance of O2 Sensors
Imagine a car engine as a hungry beast constantly seeking the perfect diet of air and fuel. The O2 sensor acts as the engine’s taste buds, sampling the exhaust gases and informing the ECU about the fuel-air ratio. This information is crucial for the ECU to adjust the fuel injection system and maintain optimal engine performance.
How to Check O2 Sensor with a Scan Tool
Checking an O2 sensor with a scan tool is a straightforward process. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
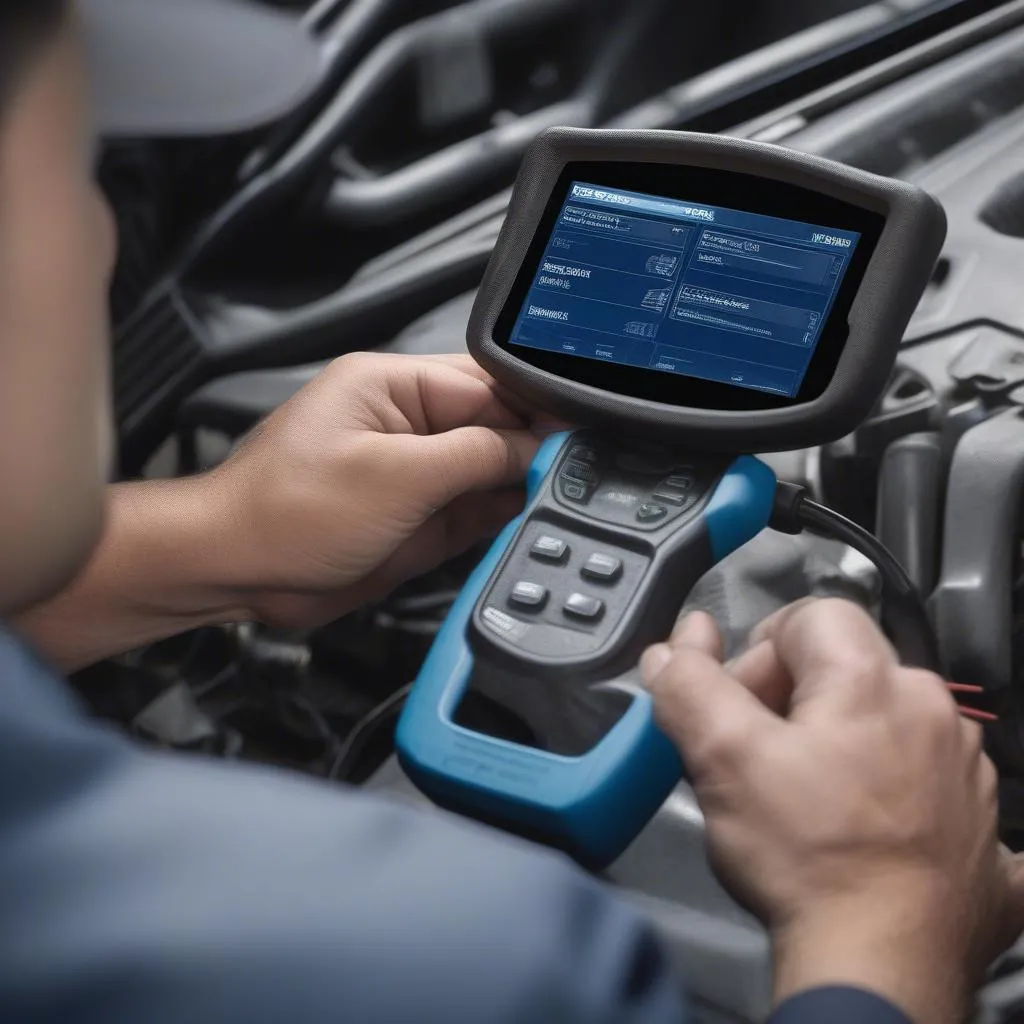
1. Connect the Scan Tool
The first step is to connect your scan tool to the car’s diagnostic port, usually located under the dashboard. Most modern scan tools are compatible with OBDII (On-Board Diagnostics II) protocols, which are standard across various car manufacturers.
2. Navigate to Live Data
Once the scan tool is connected, navigate to the “Live Data” or “Data Stream” section. This will display real-time data from various sensors, including the O2 sensor.
3. Identify the O2 Sensor Data
Locate the O2 sensor readings on the live data screen. Depending on the scan tool and the vehicle’s model, the data may be displayed in various ways, such as:
- Voltage: The O2 sensor’s output is typically measured in volts, ranging from 0.1 to 0.9 volts.
- Lambda: The O2 sensor reading can also be displayed as a lambda value, which represents the ratio of air to fuel.
4. Analyze the O2 Sensor Readings
Here’s what you should look for when analyzing the O2 sensor data:
- Switching Frequency: A healthy O2 sensor should switch between 0.1 and 0.9 volts (or equivalent lambda values) frequently, indicating that it is correctly monitoring the exhaust gases.
- Response Time: The O2 sensor should respond quickly to changes in the exhaust gas composition. If the sensor is slow to react, it may be faulty.
- Stuck at a Specific Value: If the O2 sensor reading is stuck at a fixed value, it could be a sign of a defective sensor.
5. Interpreting the Results
If the O2 sensor readings appear to be erratic, unresponsive, or stuck, it suggests a problem with the sensor itself or the wiring. Consult a qualified mechanic for further diagnosis and repair.
Common O2 Sensor Issues and How to Troubleshoot Them
While checking the O2 sensor with a scan tool provides valuable insights, it’s important to understand common O2 sensor issues and how to troubleshoot them.
- O2 Sensor Contamination: Exhaust gases can deposit soot and other contaminants on the O2 sensor’s tip, affecting its readings. This can be resolved by cleaning the sensor.
- O2 Sensor Wiring Problems: A broken or corroded wire in the O2 sensor circuit can also cause faulty readings. Inspect the wiring for damage and make necessary repairs.
- Defective O2 Sensor: In some cases, the O2 sensor itself may be defective. If you suspect this, consider replacing the sensor with a new one.
Frequently Asked Questions about O2 Sensors
Q: How often should I replace my O2 sensor?
A: The lifespan of an O2 sensor varies depending on the vehicle, driving conditions, and maintenance practices. Generally, they can last between 50,000 and 100,000 miles. However, if you notice symptoms like poor fuel economy, engine misfires, or a check engine light, it’s best to have the O2 sensor inspected.
Q: Can I check the O2 sensor without a scan tool?
A: It’s difficult to accurately diagnose an O2 sensor without a scan tool. While visual inspections can help identify external issues, a scan tool provides detailed data about the sensor’s performance.
Q: What are the signs of a bad O2 sensor?
A: Symptoms of a faulty O2 sensor include:
- Check engine light: The most common sign of a problem with the O2 sensor is a lit-up check engine light.
- Poor fuel economy: A faulty O2 sensor can lead to an overly rich or lean fuel mixture, resulting in poor fuel economy.
- Engine misfires: A faulty O2 sensor can also cause the engine to misfire, leading to rough idling or a lack of power.
- Black smoke: If the O2 sensor is malfunctioning, it can cause an overly rich fuel mixture, leading to black smoke from the exhaust.
Other Helpful Resources
For more information on using scan tools and troubleshooting O2 sensors, check out these articles:
Conclusion
Understanding how to check an O2 sensor with a scan tool can help you maintain your vehicle’s performance. By monitoring the sensor readings and identifying any issues early on, you can prevent more serious problems from developing. If you’re unsure about anything, it’s always best to consult a qualified mechanic.
If you need assistance with setting up diagnostic tools or have any questions about O2 sensors, don’t hesitate to contact us! Our team of experts is available 24/7 to provide guidance and support.
WhatsApp: +84767531508
 oxygen sensor readings
oxygen sensor readings
 locating an oxygen sensor
locating an oxygen sensor
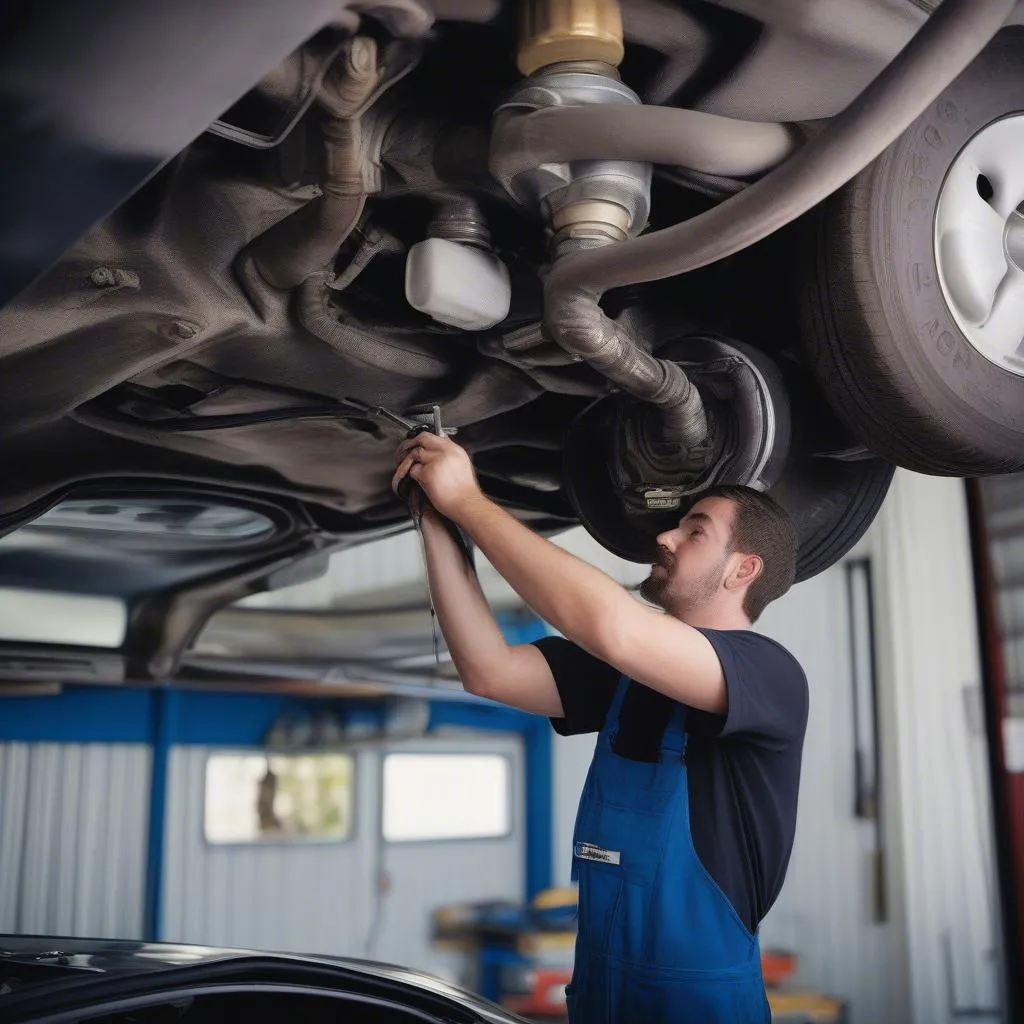 Replacing an oxygen sensor
Replacing an oxygen sensor