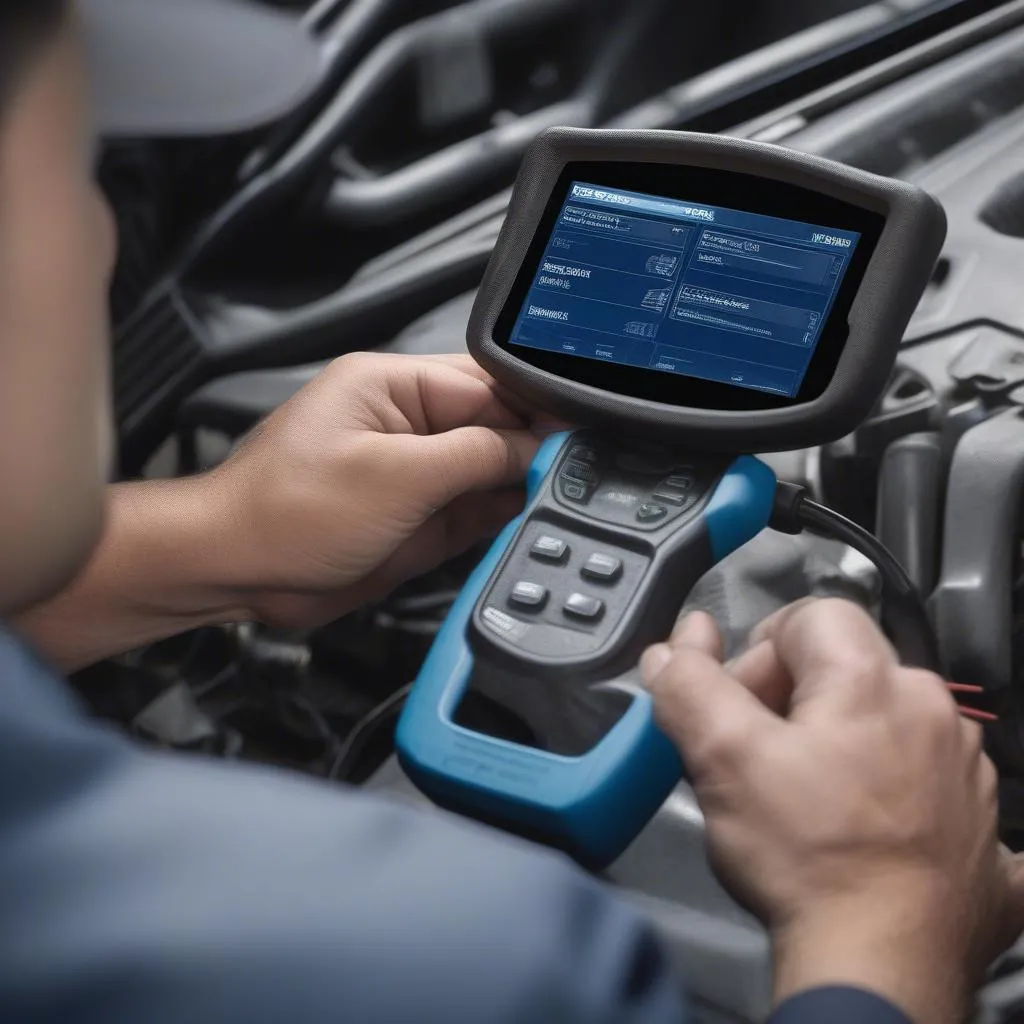
Ever wondered how to check for a bad catalytic converter using a scan tool? You’re not alone. Many car owners encounter problems with their catalytic converters, and often the first sign is a check engine light that won’t go away. While a scan tool can’t definitively tell you if your catalytic converter is bad, it can provide crucial clues that point you in the right direction.
What is a Catalytic Converter?
To fully understand how to check for a bad cat, let’s first delve into what it is and its function.
Think of a catalytic converter as a small, cylindrical “silencer” attached to your car’s exhaust system. It’s a critical component that plays a vital role in reducing harmful emissions from your engine. Imagine a scenario where you’re driving on a bustling highway in Los Angeles, California. Your car is emitting harmful exhaust gases, but thanks to the catalytic converter, those gases are converted into less harmful ones.
Why it’s important to check for a bad catalytic converter?
The catalytic converter is a valuable part of your car’s emission system. It’s essential for reducing harmful gases like carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides, and hydrocarbons.
Now, imagine a scenario where you’re in a beautiful national park like Yellowstone National Park in Wyoming. You’d want to ensure your car is emitting clean air, right? If your catalytic converter isn’t working properly, it can lead to increased emissions, impacting the environment and potentially failing an emissions test.
How to Check for a Bad Catalytic Converter Using a Scan Tool
Let’s dive into the practical aspects of checking for a bad cat using a scan tool.
Understanding Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
The first step is to use a scan tool to read your car’s Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs). These codes are like little messages from your car’s computer, telling you about any issues it detects.
Imagine a scenario where you’re driving your car in Chicago, Illinois, and the check engine light comes on. You pull over, grab your scan tool, and discover a DTC related to your catalytic converter. Now, this doesn’t necessarily mean your cat is bad, but it’s a significant sign that something might be wrong.
Identifying Relevant DTCs for Catalytic Converter Issues
Here are some common DTCs that might indicate a problem with your catalytic converter:
- P0420 – Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1)
- P0430 – Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 2)
- P0421 – Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1)
- P0431 – Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 2)
- P0432 – Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 2)
- P0433 – Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 2)
- P0434 – Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 2)
- P0435 – Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 2)
- P0436 – Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 2)
- P0437 – Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 2)
- P0438 – Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 2)
- P0439 – Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 2)
Analyzing the DTCs and Looking for Clues
Let’s get back to that scenario in Chicago. You’ve identified a DTC related to your catalytic converter. Now, it’s time to get a little more specific.
While a scan tool can’t tell you exactly what’s wrong with your catalytic converter, it can often point you in the right direction. You can check if the DTC is related to a specific bank of cylinders or if it’s a general code. This will give you a better idea of the area of the exhaust system you need to focus on.
Other Diagnostic Steps
In addition to analyzing the DTCs, there are other diagnostic steps you can take to help identify the root cause of the problem:
- Check for exhaust leaks: Look for any leaks in the exhaust system, which can indicate damage or wear.
- Monitor fuel trim values: These values provide insights into how much fuel the engine is injecting to achieve the desired air-fuel ratio.
- Perform a backpressure test: This test measures the pressure in the exhaust system.
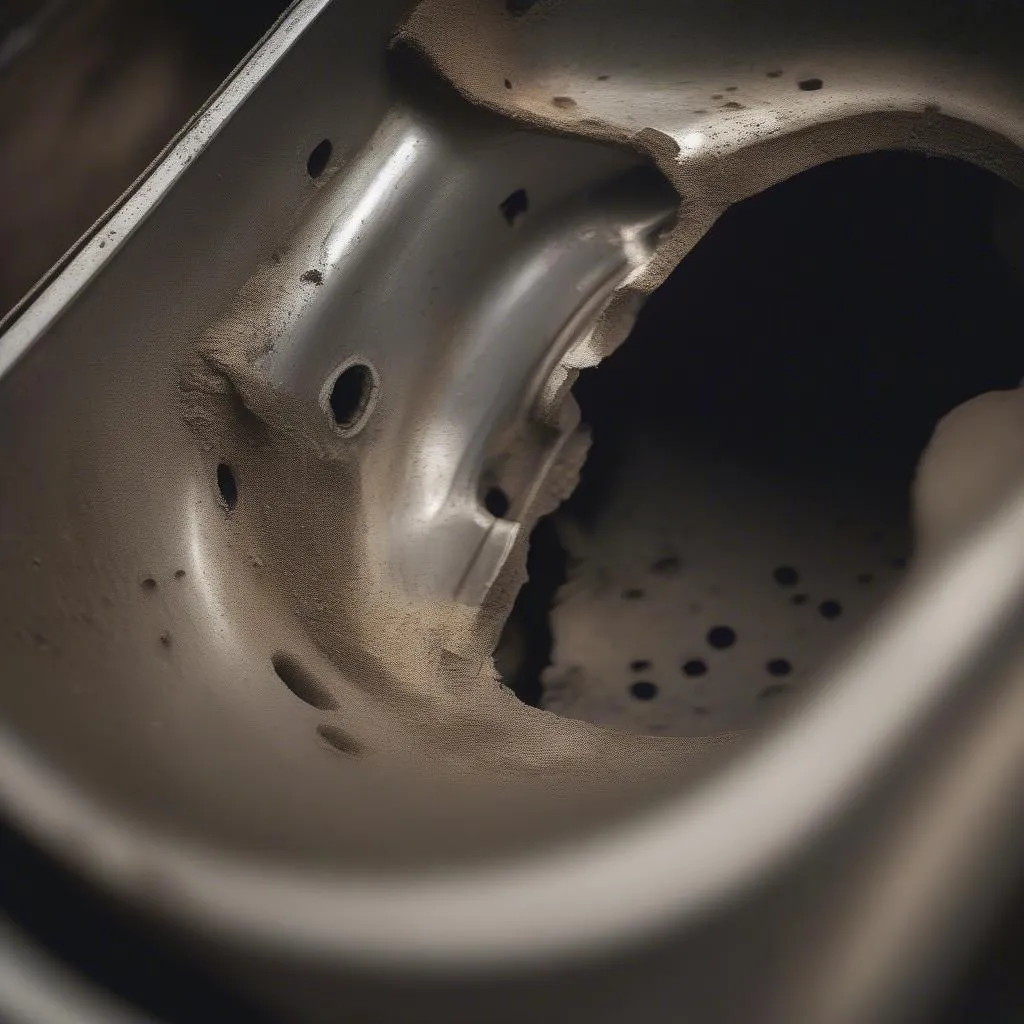 damaged-catalytic-converter
damaged-catalytic-converter
Additional Questions to Consider
Here are some additional questions that may arise when you are trying to diagnose a bad catalytic converter.
What are the signs of a bad cat converter?
Besides check engine light, some signs include a decrease in fuel economy, a rattling sound from the exhaust system, and a strong odor of exhaust fumes.
Can I drive my car with a bad cat converter?
Driving with a bad cat can lead to increased emissions and damage to your engine.
How much does it cost to replace a cat converter?
The cost of replacing a catalytic converter can vary depending on the make and model of your car.
What are the alternatives to replacing a cat converter?
Some alternatives include repairing a damaged cat converter, but it’s usually more cost-effective to replace it.
Can I use a generic catalytic converter?
While there are generic cat converters available, it’s best to use a manufacturer-specific one for optimal performance.
How to find a reliable mechanic?
You can ask for recommendations from friends, family, or your local auto parts store.
 new-catalytic-converter
new-catalytic-converter