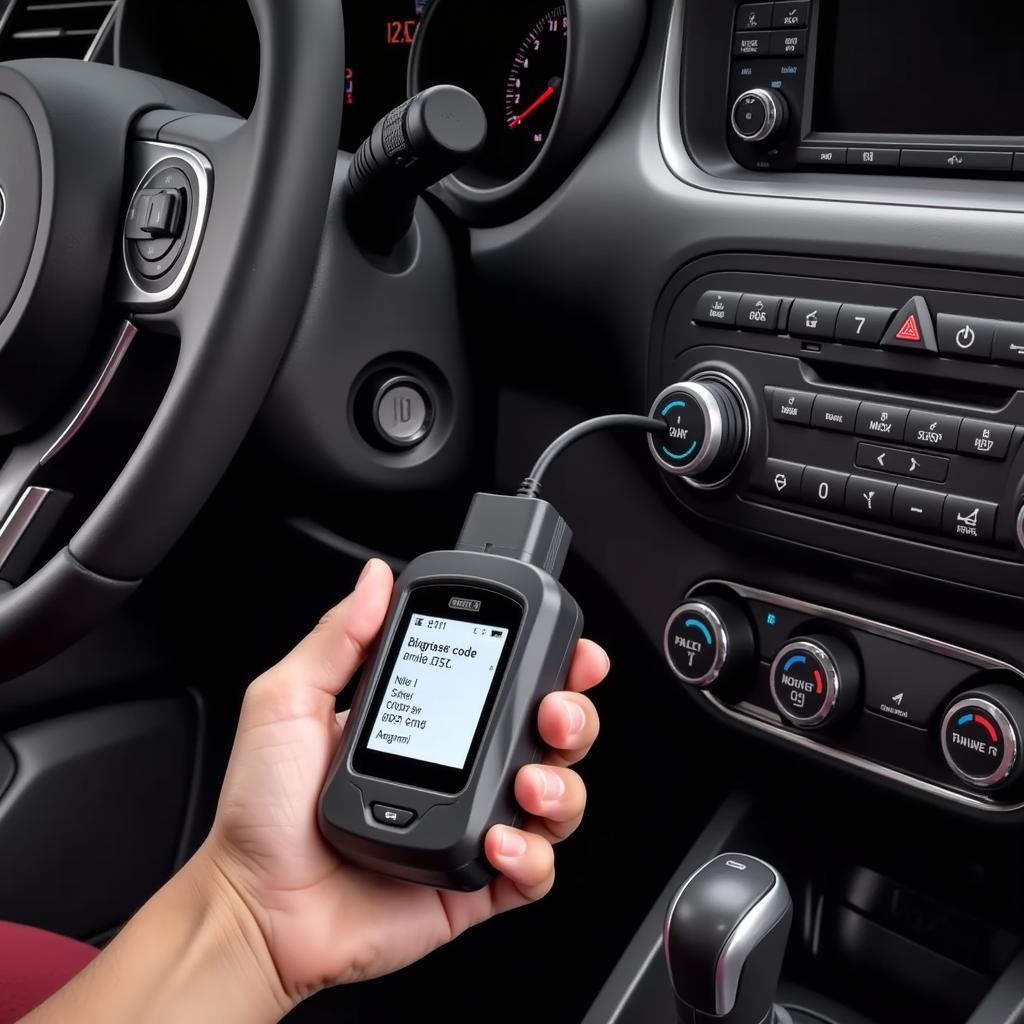
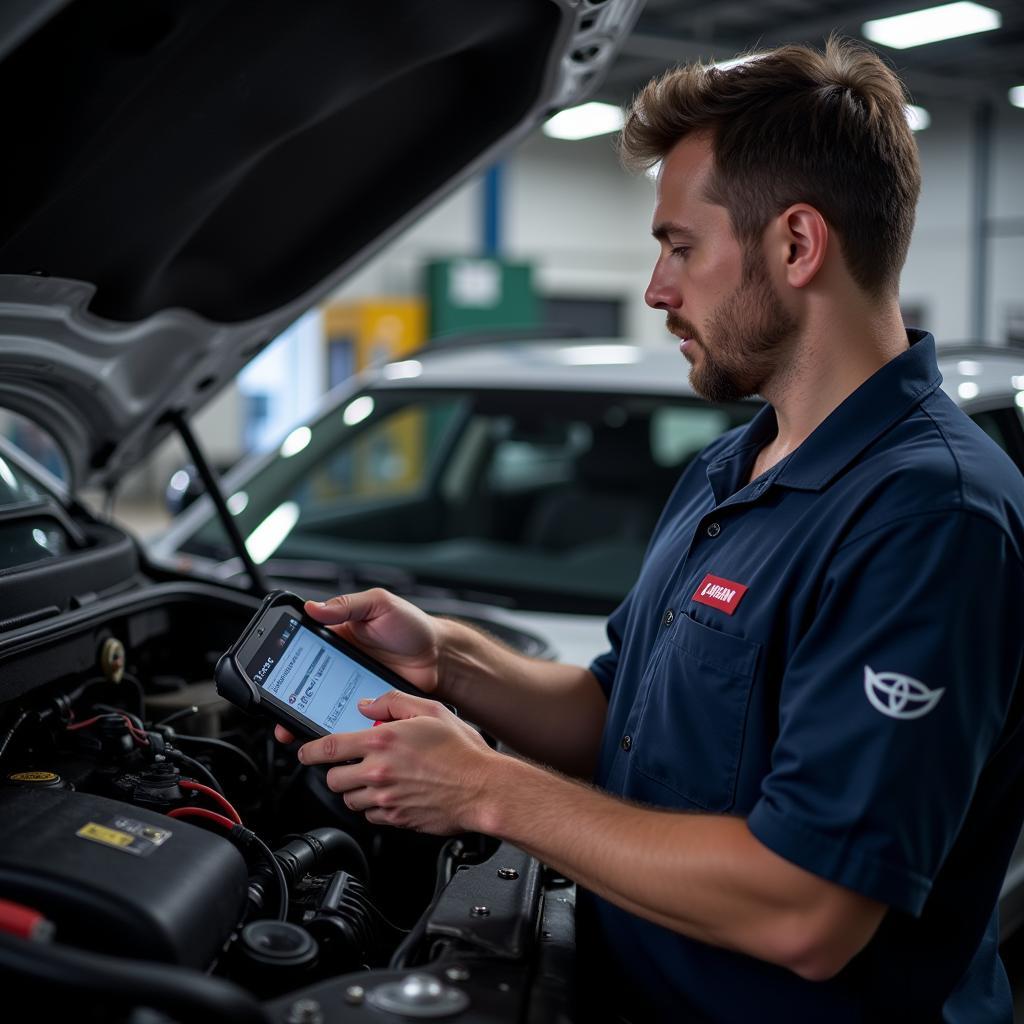
Testing an EGR valve for restriction is a crucial aspect of maintaining your vehicle’s engine performance and emissions control. The EGR (Exhaust Gas Recirculation) system plays a vital role in reducing harmful NOx emissions by redirecting a controlled amount of exhaust gases back into the intake manifold. A restricted EGR valve can disrupt this process, leading to a cascade of engine problems. Thankfully, with the right scan tool, diagnosing and addressing EGR valve restrictions can be a straightforward process. This guide will delve into the intricacies of EGR valve operation, the common symptoms of a restricted valve, and how to use a scan tool to accurately identify and rectify this issue.
Understanding the EGR Valve and Its Function
The EGR valve acts as a gatekeeper between the exhaust manifold and the intake manifold. When operating correctly, it allows a measured flow of exhaust gases to mix with the incoming fresh air. This mixture, being oxygen-depleted, helps lower combustion temperatures within the cylinders. Reducing combustion temperatures effectively diminishes the production of harmful NOx emissions, contributing to a cleaner environment.
Signs of a Restricted EGR Valve: When to Suspect Trouble
A restricted EGR valve often manifests itself through noticeable symptoms, signaling the need for immediate attention. Keep an eye out for the following signs, which could indicate a problem:
- Check Engine Light Illumination: One of the most common indicators is the illumination of the check engine light on your dashboard. This warning signal should never be ignored.
- Rough Idle and Engine Stalling: A restricted EGR valve can disrupt the air-fuel mixture, leading to a rough idle and even engine stalling, particularly during deceleration or when idling.
- Increased NOx Emissions: As the EGR valve’s ability to regulate exhaust gas recirculation is compromised, NOx emissions can increase, potentially leading to failed emissions tests.
- Reduced Fuel Efficiency: A noticeable decrease in fuel efficiency may point towards a restricted EGR valve, as it disrupts the engine’s optimal air-fuel ratio.
- Engine Knocking or Pinging: The pre-ignition of the air-fuel mixture due to a restricted EGR valve can cause a knocking or pinging sound from the engine.
The Power of a Scan Tool in EGR Valve Diagnosis
While the symptoms mentioned above can point to a potential EGR valve restriction, a scan tool provides the most accurate and efficient way to diagnose the issue. Here’s why:
- Reading Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs): A scan tool can read the diagnostic trouble codes stored in your vehicle’s Engine Control Unit (ECU). These codes act as specific indicators, often directly related to EGR system malfunctions, including a restricted EGR valve.
- Monitoring Live Data Stream: Scan tools allow you to access live data streams from various sensors, including the EGR valve position sensor. This real-time information provides insights into the valve’s response to commands from the ECU.
- Performing Active Tests: Advanced scan tools often include functionality for performing active tests on the EGR system. These tests can command the EGR valve to open and close, allowing you to observe its movement and identify any restrictions.
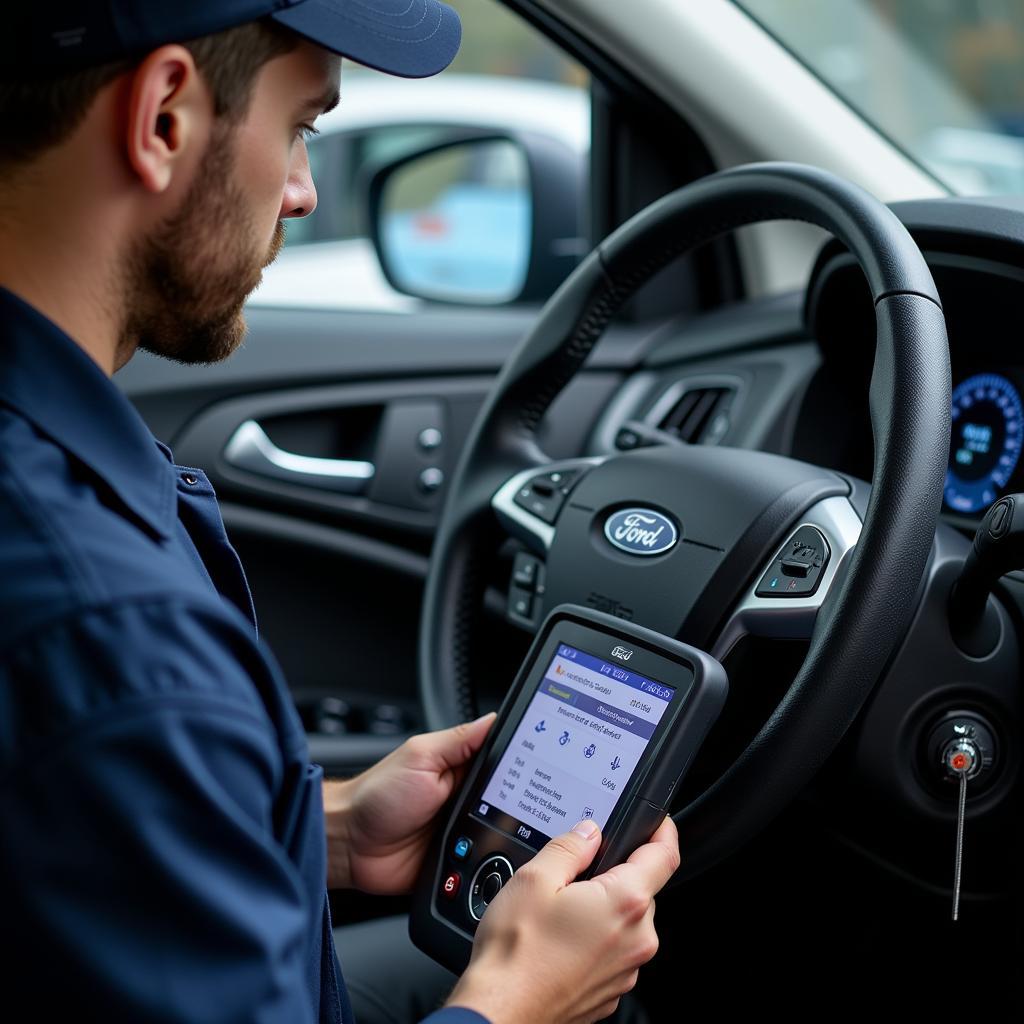
 Mechanic using a scan tool to diagnose an EGR valve restriction
Mechanic using a scan tool to diagnose an EGR valve restriction
How to Test for EGR Valve Restriction with a Scan Tool
Follow these general steps to test for an EGR valve restriction using a scan tool:
- Connect the Scan Tool: Begin by safely parking your vehicle and turning off the engine. Locate the OBD-II port, usually found under the dashboard on the driver’s side. Connect your scan tool to the port.
- Turn on the Ignition: Turn the ignition to the “On” position without starting the engine. This powers up the scan tool and allows it to communicate with the vehicle’s ECU.
- Read Diagnostic Trouble Codes: Access the scan tool’s menu and select the option to read DTCs. Note down any codes related to the EGR system, as these provide valuable clues about the specific problem.
- Access Live Data Stream: Navigate to the live data stream section of your scan tool. Look for parameters related to the EGR system, such as “EGR Valve Position,” “EGR Command,” and “EGR Flow Rate.”
- Monitor EGR Valve Position: Observe the EGR valve position reading while the engine is idling. Ideally, the valve should show a percentage of opening as commanded by the ECU. If the position remains at 0% or shows very little movement, it could indicate a restriction.
- Perform Active Tests (If Available): If your scan tool offers active test capabilities, locate the EGR valve test. This test typically commands the valve to open and close. Observe the live data stream for changes in EGR valve position and flow rate during the test. Significant deviations from expected values could suggest a restriction.
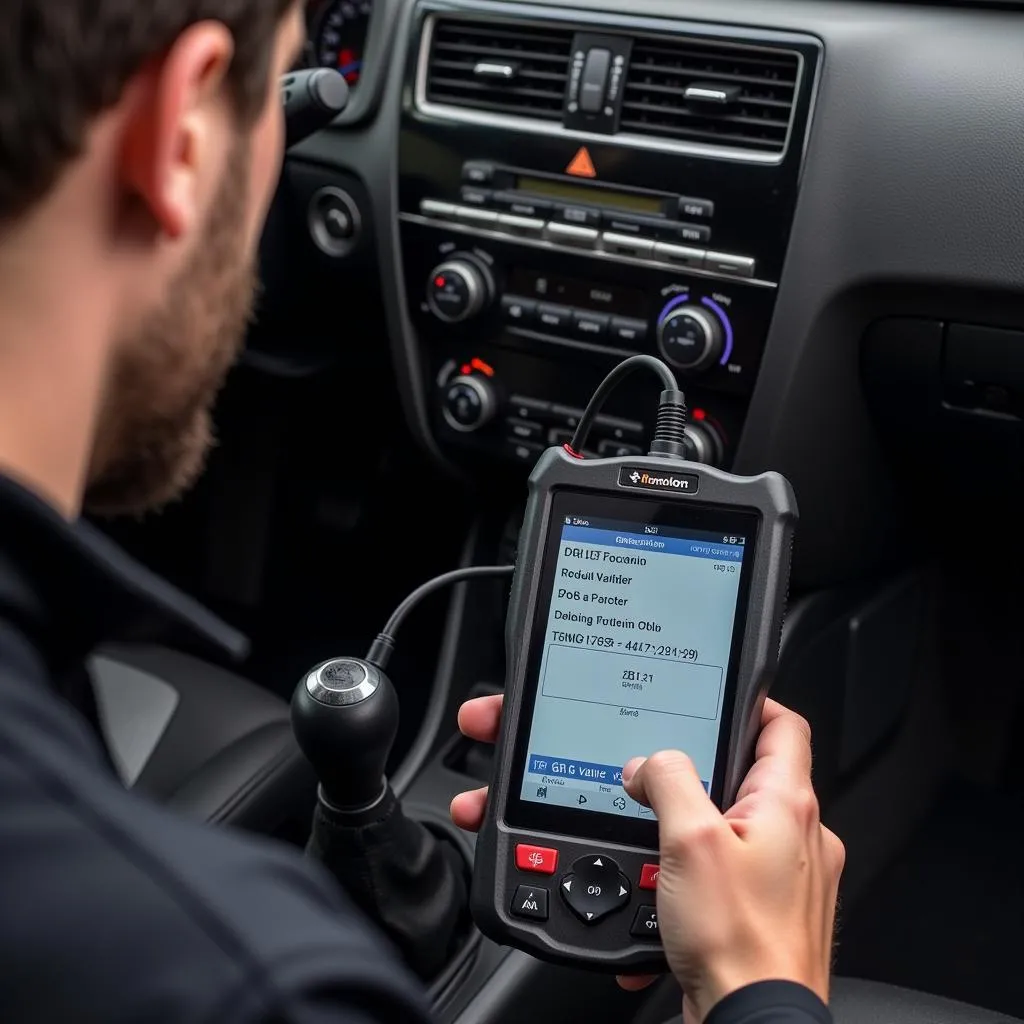
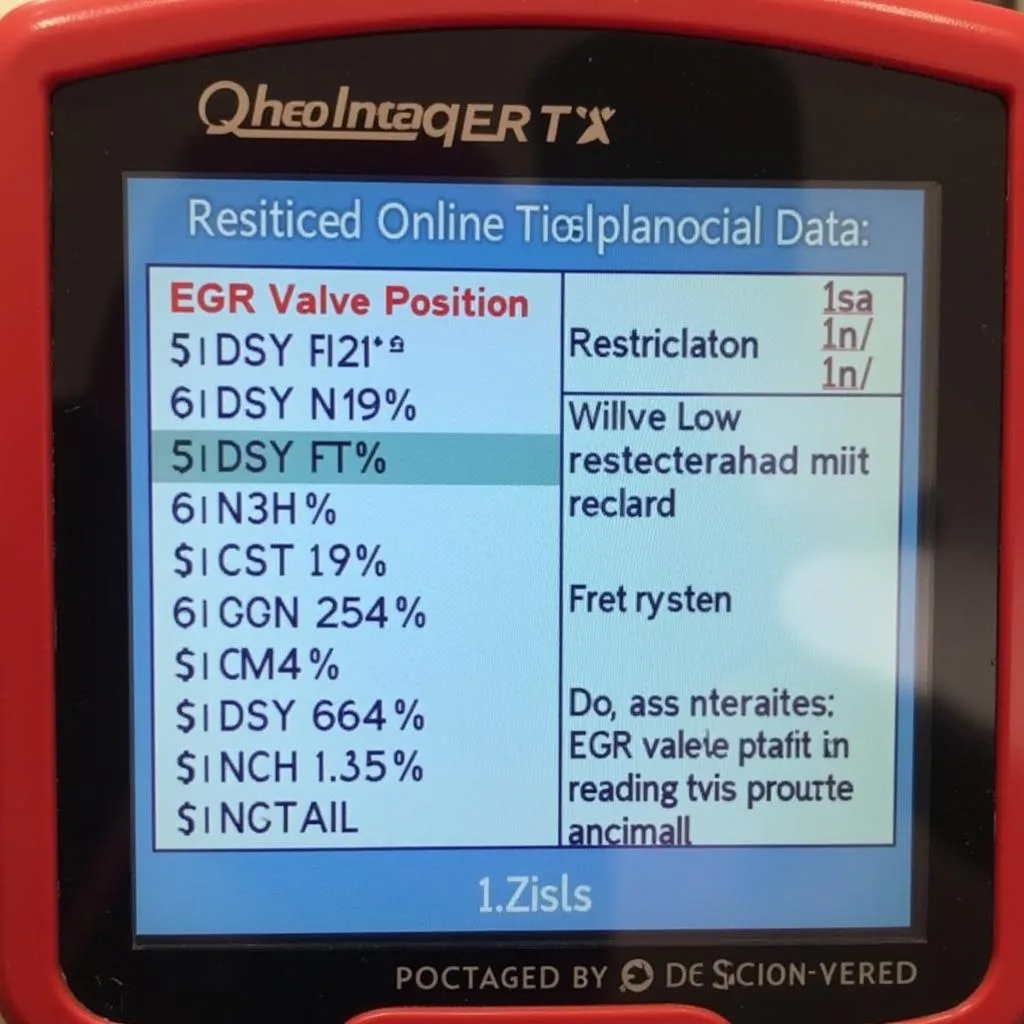 Close-up of a scan tool screen displaying EGR valve data
Close-up of a scan tool screen displaying EGR valve data
Interpreting the Results: Identifying a Restriction
After performing the tests, carefully analyze the data collected by the scan tool:
- No Change in EGR Valve Position: If the EGR valve position remains unchanged despite commands from the ECU or during active tests, it strongly suggests a mechanical restriction within the valve itself.
- Sluggish EGR Valve Response: A slow or hesitant response to commands may indicate a partial restriction in the valve or its associated passages.
- Inconsistent EGR Flow Rate: Fluctuations or inconsistencies in the EGR flow rate data, particularly during active tests, can also point towards a restriction.
Beyond the Scan Tool: Further Inspection
While a scan tool is invaluable for initial diagnosis, confirming a restricted EGR valve often requires a visual inspection:
- Visual Examination: With the engine off and cool, locate the EGR valve. Inspect the valve and its connecting hoses or pipes for any visible signs of blockage, carbon buildup, or damage.
- Vacuum Hose Inspection: If your EGR system uses vacuum hoses for control, check these hoses for cracks, leaks, or disconnections. These issues can disrupt the vacuum pressure needed to operate the valve correctly.
Addressing the Issue: Resolving EGR Valve Restrictions
The solution to a restricted EGR valve depends on the underlying cause. Here are some common approaches:
- EGR Valve Cleaning: In cases of carbon buildup, cleaning the EGR valve and its passages might be sufficient. This typically involves removing the valve, soaking it in a specialized cleaner, and using a brush to remove deposits.
- EGR Valve Replacement: If the valve itself is damaged or severely restricted, replacement is often necessary. When replacing the EGR valve, it’s also advisable to replace the gasket to ensure a proper seal.
- Vacuum Hose Repair or Replacement: If inspection reveals damaged or leaking vacuum hoses, repair or replacement is crucial to restoring proper EGR system operation.
The Importance of Regular Maintenance
Preventing EGR valve restrictions is far more efficient and cost-effective than addressing them after they occur.
- Regular Engine Tune-Ups: Include EGR system inspections as part of your vehicle’s routine maintenance schedule.
- Use High-Quality Fuel: Opt for high-quality fuel and consider using fuel additives designed to reduce carbon buildup in the engine and EGR system.
 Mechanic cleaning a car EGR valve
Mechanic cleaning a car EGR valve
Conclusion: Keeping Your Engine Healthy
Testing an EGR valve for restriction with a scan tool is a vital skill for any car owner or mechanic. Understanding how to interpret the data provided by these tools empowers you to diagnose and address EGR valve issues effectively. Remember that regular maintenance and timely repairs are essential for maximizing your vehicle’s performance, fuel efficiency, and longevity. By taking a proactive approach to EGR valve maintenance, you can ensure a smooth-running and environmentally friendly driving experience for miles to come.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Can I drive with a restricted EGR valve?
While technically possible, it’s highly discouraged to drive with a restricted EGR valve. Doing so can lead to further engine damage, decreased fuel efficiency, and increased harmful emissions.
2. How often should I clean my EGR valve?
The recommended cleaning interval varies depending on your vehicle model and driving habits. However, it’s generally advisable to have the EGR valve inspected and cleaned, if necessary, every 30,000 to 50,000 miles.
3. Can a faulty EGR valve cause a no-start condition?
While uncommon, a severely malfunctioning EGR valve can contribute to a no-start condition in some cases. If the valve is stuck open, it can disrupt the air-fuel mixture to the point where the engine cannot ignite.
4. Are there any risks associated with cleaning the EGR valve myself?
Cleaning the EGR valve involves handling engine components, and improper handling can potentially cause damage. If you’re unsure about the process, it’s best to consult a qualified mechanic.
5. What is the typical cost of replacing an EGR valve?
The cost of EGR valve replacement varies based on the vehicle make and model and labor rates in your area. On average, you can expect to pay between $200 and $500 for the replacement, including parts and labor.
Need Assistance with Your EGR Valve or Scan Tool Needs?
Don’t hesitate to contact us! Our team of automotive experts is available 24/7 to provide support and guidance. Reach us via:
- WhatsApp: +1(641)206-8880
- Email: [email protected]
- Visit Our Workshop: 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States.
We’re here to help you keep your vehicle running smoothly and efficiently. Explore our website for a wide range of high-quality scan tools and automotive diagnostic solutions. You might also be interested in our article on 2004 6.0 powerstroke scan tool for specific diagnostic needs related to your Powerstroke engine.


