Imagine you’re working on a European car, and the engine isn’t starting. You’ve checked all the usual suspects – fuel, spark, and compression – but nothing seems to be amiss. You suspect a problem with the crankshaft position system, but you don’t have a scan tool to help you diagnose the issue. What do you do?
Understanding the Importance of the Crankshaft Position System
The crankshaft position system is crucial for the smooth operation of any internal combustion engine. It’s responsible for providing the engine control unit (ECU) with information about the position of the crankshaft, which is essential for timing the ignition and fuel injection.
Why is a Scan Tool Necessary?
While a scan tool can be helpful, it’s not always necessary to diagnose and troubleshoot problems with the crankshaft position system. Many automotive technicians have gained a deep understanding of these systems and can troubleshoot them without the aid of a scan tool. For instance, “The ability to diagnose and repair these systems without a scan tool demonstrates a mastery of the intricate workings of the engine,” says automotive expert David Williams.
Diagnosing and Troubleshooting Crankshaft Position System Issues Without a Scan Tool
1. The “Basic” Diagnostic Approach:
-
Visual Inspection: Start by visually inspecting the crankshaft position sensor (CPS) and its wiring for any obvious signs of damage, such as broken wires, corrosion, or loose connections.
-
Check for Continuity: If you have a multimeter, you can check for continuity in the CPS circuit to ensure that the sensor is working properly.
-
Check for Signal: You can use a digital oscilloscope to check for a signal from the CPS.
-
Checking Engine Timing: Using a timing light, you can verify the timing marks on the crankshaft and camshaft are aligned correctly. This can help you determine if the timing belt or chain is out of sync.
-
Identify Potential Problems: Based on the results of the visual inspection, continuity checks, signal checks, and engine timing checks, you can start to identify potential problems with the crankshaft position system. For example, if you find that the CPS is damaged, then you know that you need to replace the sensor.
2. The “More Advanced” Diagnostic Approach:
-
Engine Mechanical Check: This involves checking for any mechanical problems with the crankshaft itself, such as a broken crankshaft or a damaged crankshaft bearing. This might require removing the engine pan to examine the crankshaft.
-
ECU Checks: You can check the ECU for any error codes, which could indicate problems with the crankshaft position system. While a scan tool is the usual method for this, some manufacturers allow for simple “in-car” diagnostic methods that utilize indicators like the dashboard or instrument cluster.
-
Wiring Checks: Since the crankshaft position system operates with electrical signals, you can check for any loose or broken wires in the wiring harness leading to and from the crankshaft position sensor. Using a wiring diagram and a multimeter can help pinpoint potential shorts or open circuits.
-
Checking the Reference Signal: Some crankshaft position sensors work in conjunction with a reference signal. You may need to test the reference signal using a digital oscilloscope to ensure it’s functioning properly.
For a better understanding of the visual inspection process, here’s what you might be looking for: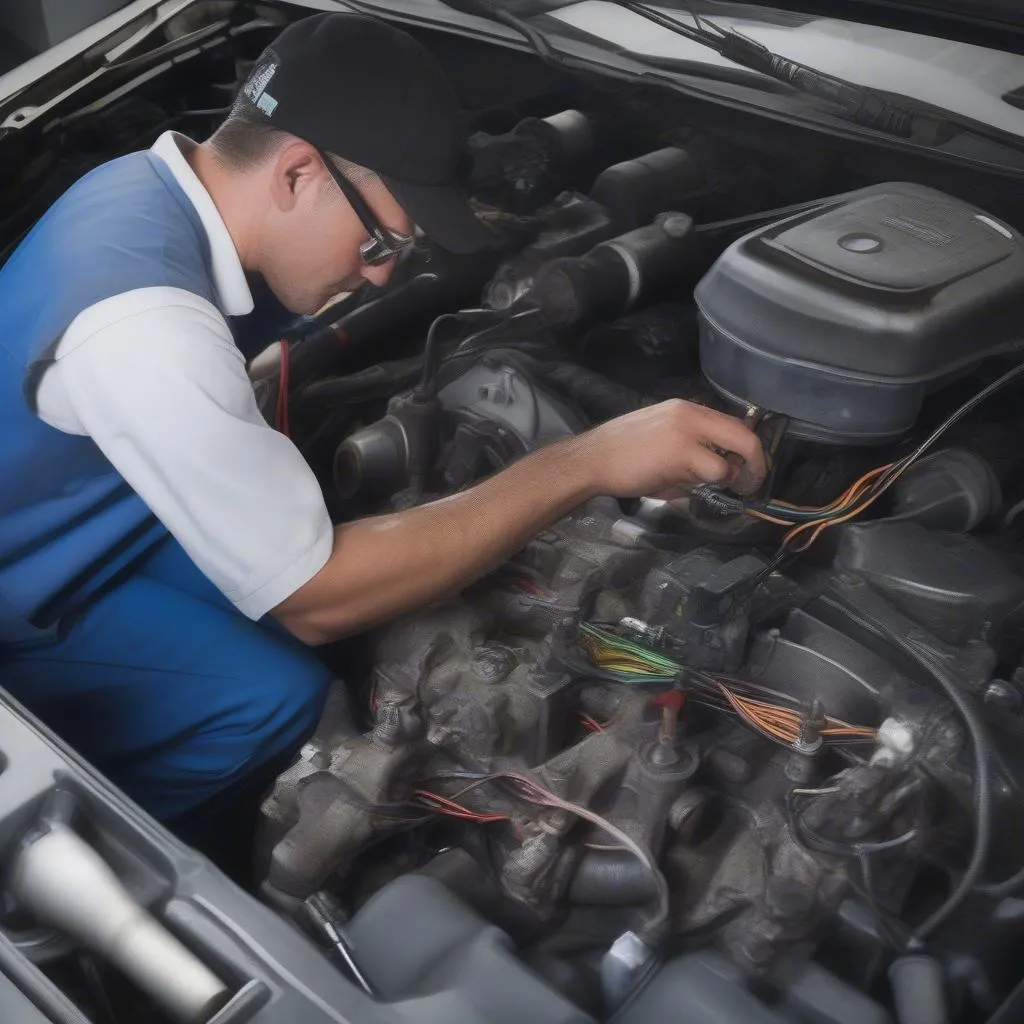  Crankshaft Position Sensor Inspection
Crankshaft Position Sensor Inspection
3. The “No Tools” Diagnostic Approach:
-
Listening to the Engine: Experienced mechanics can often identify the issue by listening to the engine. For instance, a misfire pattern can often be related to a crankshaft position sensor issue.
-
Looking for “Symptoms”: Observe if the car starts but then dies, starts only intermittently, runs roughly, or has a high idle. These are common symptoms associated with a faulty crankshaft position system.
-
Observing Engine Behaviour: Pay attention to the engine behavior at start-up, acceleration, and deceleration. This can help you narrow down the potential problem areas within the crankshaft position system.
For a visual representation of a typical crankshaft position sensor, check out this image: 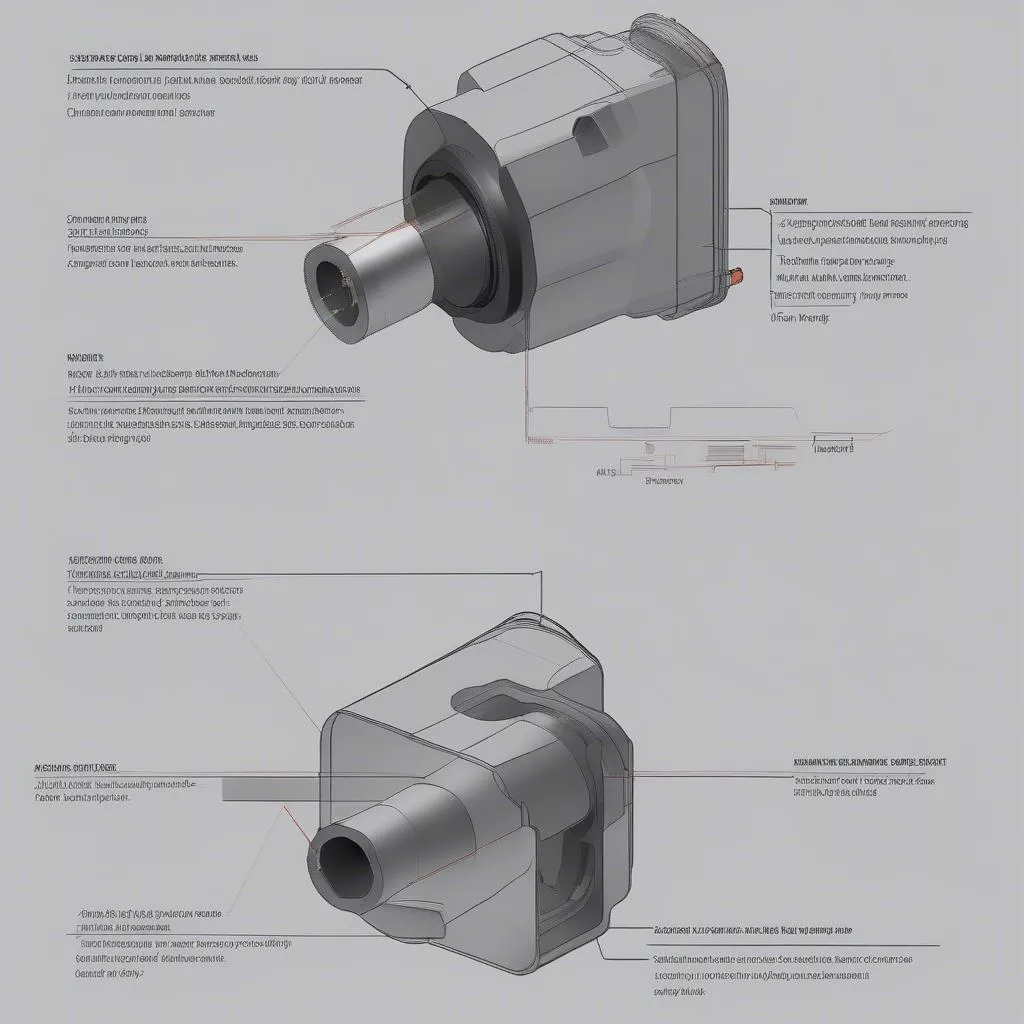 Crankshaft Position Sensor
Crankshaft Position Sensor
Learn More:
- Crankshaft Variation Relearn Procedure Without Scan Tool: This article provides a step-by-step guide to re-learning the crankshaft variation without a scan tool.
- Learn Crank Position Sensor GM Autel: This article explores the specifics of the GM crank position sensor, focusing on how to diagnose and troubleshoot issues with the Autel scan tool.
Crankshaft Position System Variation Learn Procedure Without Scan Tool: Frequently Asked Questions
1. How do I know if my crankshaft position system is faulty?
You may have a faulty system if you experience engine stalling, misfires, difficulty starting, or the check engine light is on.
2. Can I replace the crankshaft position sensor myself?
While it’s possible, it’s best to have it done by a qualified mechanic.
3. How often should I check my crankshaft position sensor?
You should check it during routine maintenance or if you experience any problems with the engine.
4. What are the common causes of a faulty crankshaft position sensor?
Common causes include damage to the sensor, wiring issues, and oil contamination.
5. Is it possible to diagnose a faulty crankshaft position sensor with a multimeter?
Yes, you can test for continuity and voltage to determine if the sensor is receiving a signal and sending it to the ECU.
Conclusion
Diagnosing and troubleshooting a faulty crankshaft position system can be a challenge, but it’s possible with the right knowledge and techniques. While scan tools are extremely helpful, they are not always necessary. By understanding how the crankshaft position system works and utilizing basic diagnostic tools and techniques, you can often identify and fix the problem.
For a visual representation of a multimeter being used to check the continuity of a crankshaft position sensor, take a look at this: 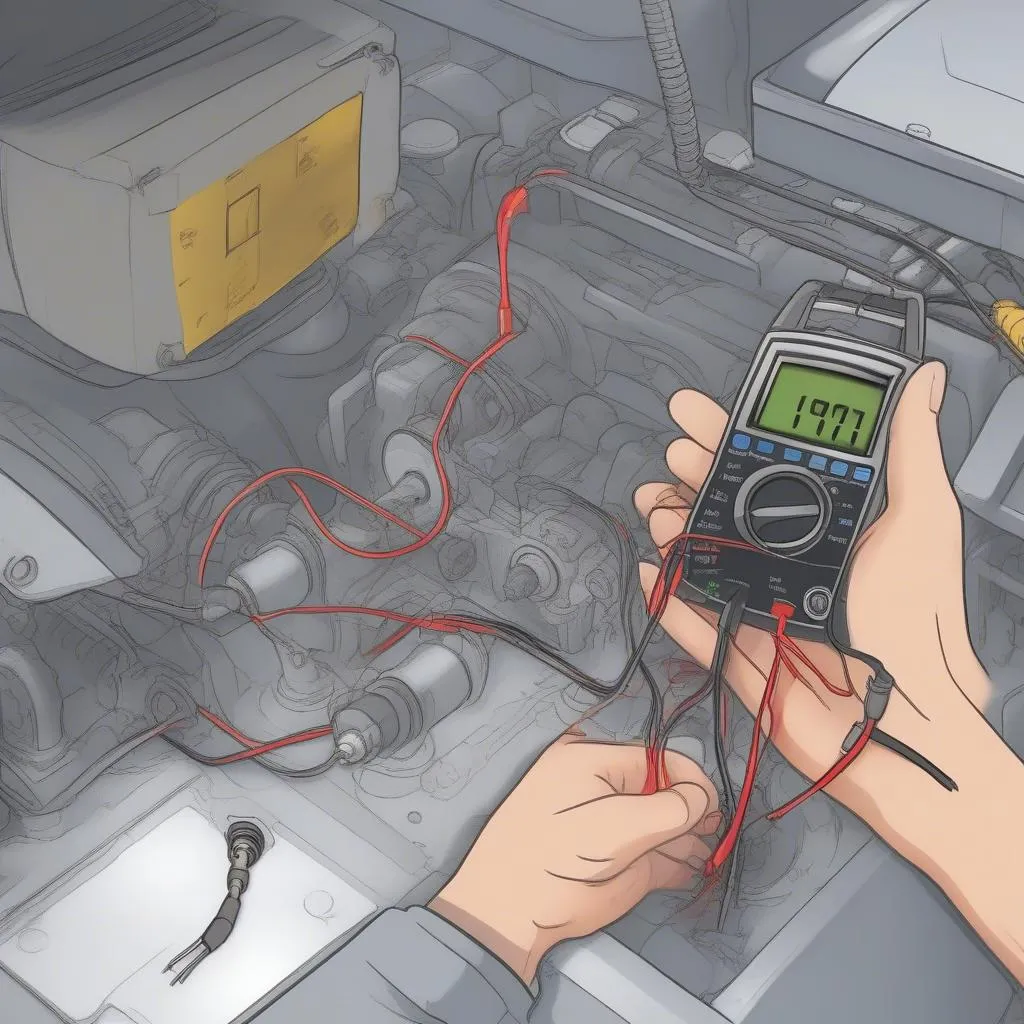 Crankshaft Position Sensor Testing with Multimeter
Crankshaft Position Sensor Testing with Multimeter
If you’re unsure, it’s always best to consult a qualified mechanic. If you’re looking for expert assistance with diagnosing or repairing crankshaft position system issues, contact Diag XCar today. Our team of experienced automotive professionals is available 24/7 to help you get your car running smoothly again.
Reach out via WhatsApp: +84767531508
Please Note: This guide is for informational purposes only and should not be taken as a substitute for professional advice. It’s crucial to have any vehicle repairs performed by a qualified mechanic.


