Begonias are prized for their colorful flowers and foliage, adding a touch of elegance and vibrancy to homes and gardens alike. While they are relatively easy to care for, understanding their specific needs can make all the difference in their health and blooming potential. This comprehensive guide delves into the essential aspects of begonias care, empowering you to cultivate these stunning plants with confidence.
Understanding Begonias: Types and Characteristics
Before diving into care tips, it’s helpful to familiarize yourself with the different types of begonias. This vast genus boasts over 1,800 species, each with unique characteristics. However, they can be broadly classified into three main categories based on their root systems:
- Tuberous Begonias: These begonias are known for their large, showy flowers that bloom in a variety of colors, including red, pink, orange, yellow, and white. They grow from tubers, which are underground storage organs.
- Fibrous Begonias: This category encompasses a wide range of begonias with fibrous roots, similar to most other plants. They are popular for their attractive foliage, which can be green, red, silver, or bronze, and often feature interesting patterns or textures. Some fibrous begonias also produce small, delicate flowers.
- Rhizomatous Begonias: These begonias develop rhizomes, which are thick, modified stems that grow horizontally underground. They are admired for their striking foliage, often showcasing intricate patterns and a wide array of colors.
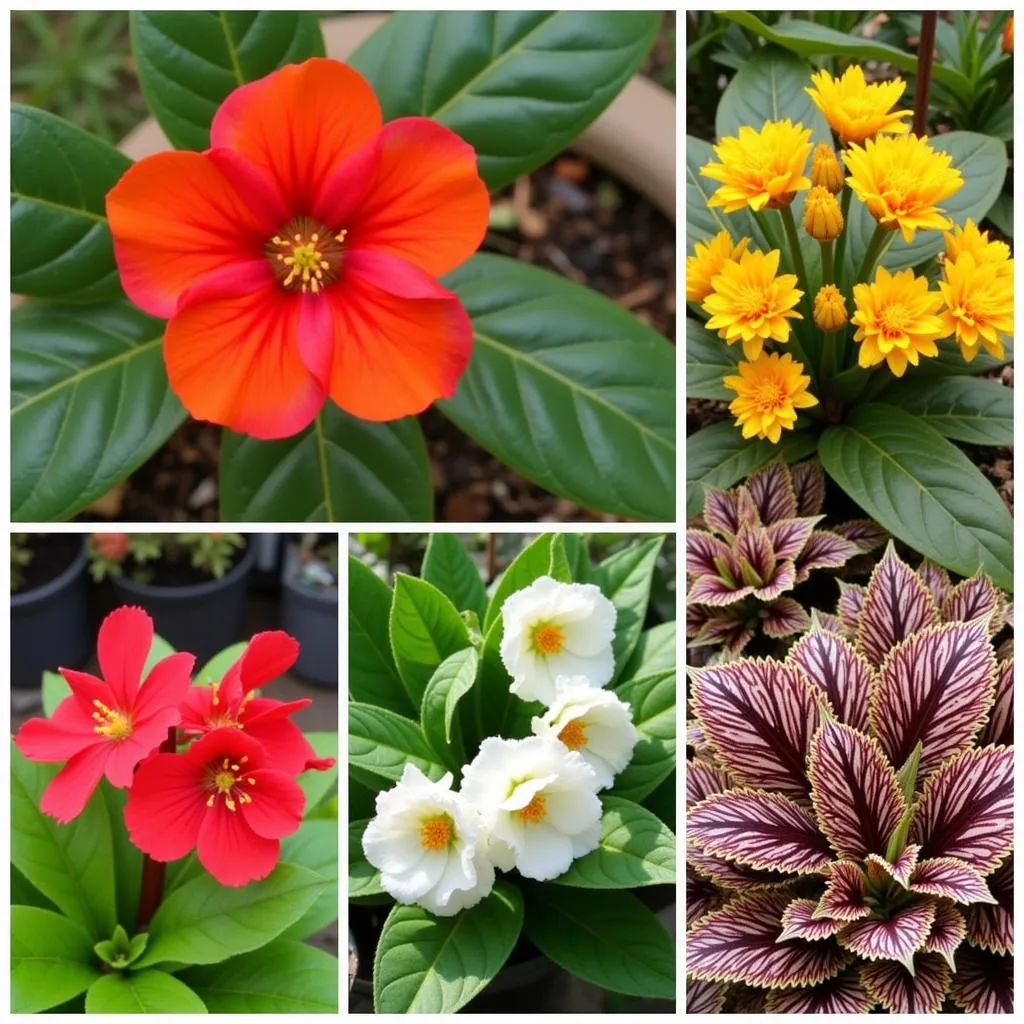 Different Types of Begonias
Different Types of Begonias
Understanding the specific type of begonia you have will provide valuable insights into its growth habits and care requirements.
Essential Begonias Care Tips
While specific care needs may vary slightly depending on the type of begonia, the following guidelines apply to most varieties:
Light Requirements:
Begonias thrive in bright, indirect light. Avoid placing them in direct sunlight, as their delicate leaves can easily scorch. East- or west-facing windows are generally ideal. If your begonias are not getting enough light, their stems may become leggy, and their growth may be stunted.
Watering:
Proper watering is crucial for healthy begonias. Overwatering can lead to root rot, a common problem that can be fatal. Water your begonias thoroughly when the top inch of soil feels dry to the touch. Allow the excess water to drain completely and avoid letting the pot sit in standing water.
 Proper Watering Technique for Begonias
Proper Watering Technique for Begonias
Humidity and Temperature:
Begonias prefer moderate to high humidity levels. If your home’s air is dry, especially during the winter months, you can increase humidity by placing the pot on a tray filled with pebbles and water. The water should not touch the bottom of the pot. Most begonias thrive in temperatures between 65°F and 75°F (18°C-24°C).
Soil and Fertilizer:
Use a well-draining, slightly acidic potting mix formulated for begonias or African violets. Fertilize your begonias every two to four weeks during the growing season (spring and summer) with a balanced, water-soluble fertilizer diluted to half strength.
Pruning and Grooming:
Regular pruning helps maintain the begonia’s shape and encourages bushier growth. Pinch off any dead or wilted flowers (deadheading) to redirect the plant’s energy towards new growth and blooms. You can also trim back leggy stems to maintain a compact form.
Common Problems and Solutions
Despite your best efforts, begonias can sometimes encounter problems. Here are some common issues and how to address them:
- Yellowing Leaves: This can be caused by overwatering, underwatering, or nutrient deficiencies. Check the soil moisture and adjust your watering schedule accordingly. If the soil is dry, water the plant thoroughly. If the soil is soggy, repot the plant in fresh, well-draining soil.
- Leaf Drop: Sudden changes in temperature, light, or humidity can cause leaf drop. Ensure consistent environmental conditions for your begonia.
- Pests: Begonias can be susceptible to pests such as mealybugs, spider mites, and aphids. Inspect your plants regularly and treat any infestations promptly with insecticidal soap or neem oil.
Propagating Begonias
One of the joys of growing begonias is the ease with which they can be propagated, allowing you to expand your collection or share these beauties with others. Begonias can be propagated through various methods, including:
- Leaf Cuttings: Take a healthy leaf and cut it into sections, ensuring each section has a vein. Insert the cut end into a moist rooting medium, such as perlite or vermiculite.
- Stem Cuttings: Select a healthy stem with at least two nodes (bumps where leaves emerge). Remove the leaves from the bottom inch of the stem and insert it into a rooting medium.
- Division: For begonias that grow from tubers or rhizomes, you can divide them during repotting. Ensure each division has a healthy portion of roots and shoots.
 Different Methods of Begonia Propagation
Different Methods of Begonia Propagation
Conclusion
With their captivating beauty and relatively low-maintenance nature, begonias are a rewarding addition to any plant lover’s collection. By following these essential care tips, you can ensure your begonias thrive, gracing your living spaces with their vibrant colors and elegant charm for years to come.