Your car won’t start, and you’re left stranded. It’s a frustrating experience, but don’t panic. Many common issues can prevent your car from cranking or starting. This guide will help you understand the underlying reasons and equip you with the knowledge to diagnose and fix these problems.
Why Won’t My Car Start?
There are several reasons why your car may refuse to start or crank, and it’s crucial to approach troubleshooting systematically. The most common culprits include issues with the battery, starter, ignition system, and fuel system.
1. The Battery Isn’t Delivering Power
The battery is the heart of your car’s electrical system, providing the initial jolt of power needed to turn the starter motor. A dead or weak battery can prevent your car from starting.
Symptoms:
- Dim headlights: This is a telltale sign of a weak battery.
- Slow cranking: If the engine turns over slowly, the battery might not have enough power.
- Clicking sound: You may hear a clicking sound when you try to start the car, indicating that the starter motor is trying to engage but lacks the necessary power.
Solutions:
- Jump-start the battery: If the battery is simply discharged, a jump-start from another car might be enough to get you going.
- Replace the battery: If the battery is old or damaged, it’s best to replace it with a new one.
2. The Starter Motor is Faulty
The starter motor is responsible for cranking the engine, allowing it to turn over and ignite. A faulty starter motor can prevent your car from starting.
Symptoms:
- Clicking sound: A clicking sound when you try to start the car can indicate a faulty starter motor.
- No cranking: The engine might not turn over at all.
Solutions:
- Check the starter motor connections: Ensure the cables connecting the starter motor to the battery are secure.
- Replace the starter motor: If the starter motor is faulty, it needs to be replaced.
3. The Ignition System is Not Firing
The ignition system is responsible for generating the spark that ignites the fuel mixture in the engine. Problems with the ignition system, such as faulty spark plugs, ignition coil, or distributor, can prevent the engine from starting.
Symptoms:
- No spark: The engine won’t start if there’s no spark.
- Misfiring: The engine might sputter or run rough if the spark plugs are faulty.
Solutions:
- Inspect the spark plugs and wires: Check the condition of the spark plugs and wires for signs of wear or damage.
- Check the ignition coil: Ensure the ignition coil is functioning properly.
- Replace faulty components: If any components in the ignition system are faulty, they need to be replaced.
4. The Fuel System is Not Supplying Fuel
The fuel system delivers fuel to the engine, and any issues with the fuel pump, fuel filter, or fuel injectors can prevent the engine from starting.
Symptoms:
- No fuel pressure: If the fuel pump is not working, there will be no fuel pressure to the engine.
- Fuel filter blockage: A clogged fuel filter can restrict fuel flow to the engine.
- Faulty fuel injectors: Blocked or faulty fuel injectors can prevent fuel from reaching the combustion chamber.
Solutions:
- Check the fuel pump: Make sure the fuel pump is functioning properly.
- Replace the fuel filter: It’s recommended to replace the fuel filter regularly.
- Clean or replace the fuel injectors: If the fuel injectors are blocked or faulty, they may need to be cleaned or replaced.
5. The Engine is Not Getting Air
The engine requires a proper air-fuel mixture to start. Problems with the air intake, such as a blocked air filter or a vacuum leak, can prevent the engine from starting.
Symptoms:
- Blocked air filter: A clogged air filter can restrict airflow to the engine.
- Vacuum leak: A vacuum leak can disrupt the air-fuel mixture, preventing the engine from starting.
Solutions:
- Replace the air filter: Regularly replace the air filter.
- Inspect for vacuum leaks: Check for any visible signs of leaks in the air intake system.
What to Do When Your Car Won’t Start or Crank
If your car won’t start or crank, here’s a step-by-step guide to help you troubleshoot the issue:
- Check the battery: Ensure the battery terminals are clean and tight. If the battery is dead, jump-start it or replace it.
- Check the starter motor: Listen for clicking sounds, indicating a potential starter motor problem. If necessary, replace the starter motor.
- Inspect the ignition system: Check the spark plugs, wires, and ignition coil for any signs of damage or wear.
- Check the fuel system: Make sure the fuel pump is functioning, the fuel filter is clean, and the fuel injectors are working properly.
- Check the air intake: Ensure the air filter is clean and there are no vacuum leaks in the air intake system.
Seeking Professional Help
If you’re unable to diagnose and fix the problem yourself, it’s recommended to seek professional help from a qualified mechanic. They have the tools and experience to accurately pinpoint the issue and make the necessary repairs.
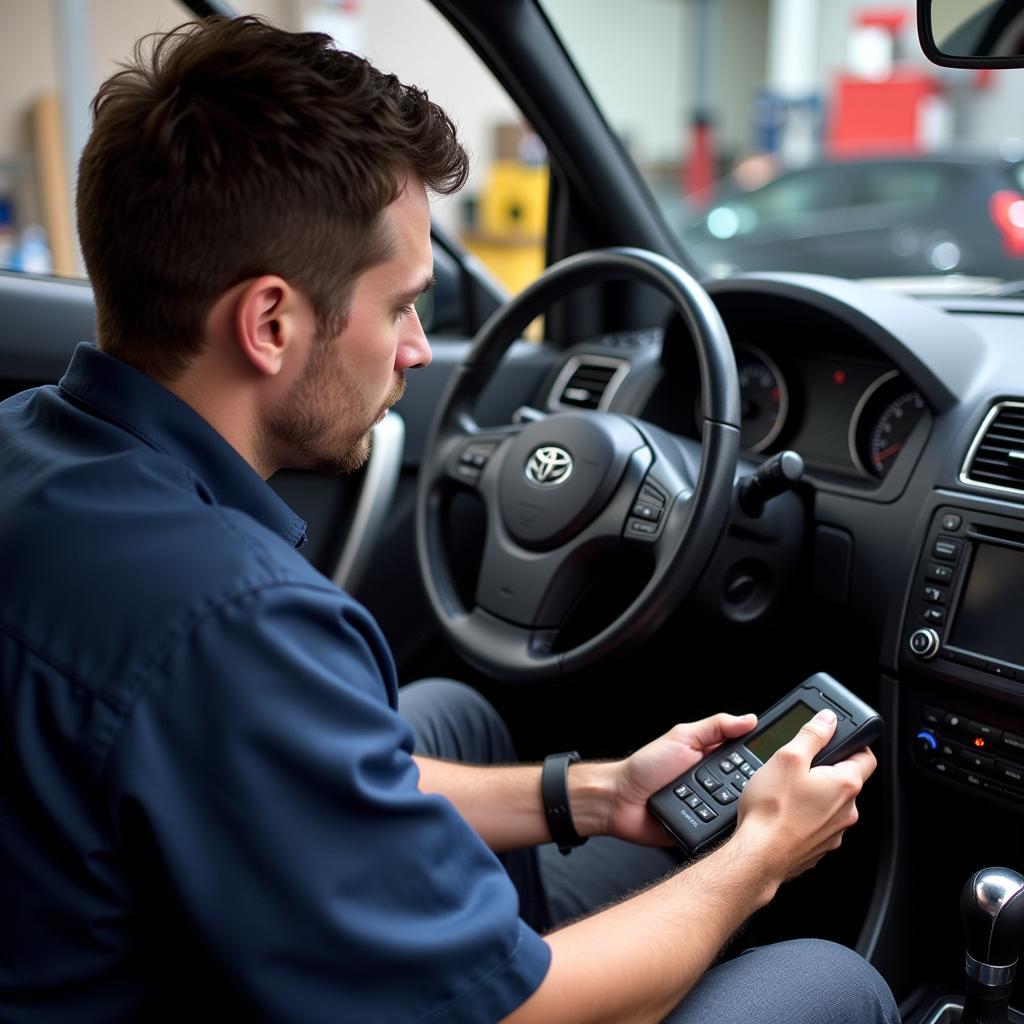 Car Diagnostics Check
Car Diagnostics Check
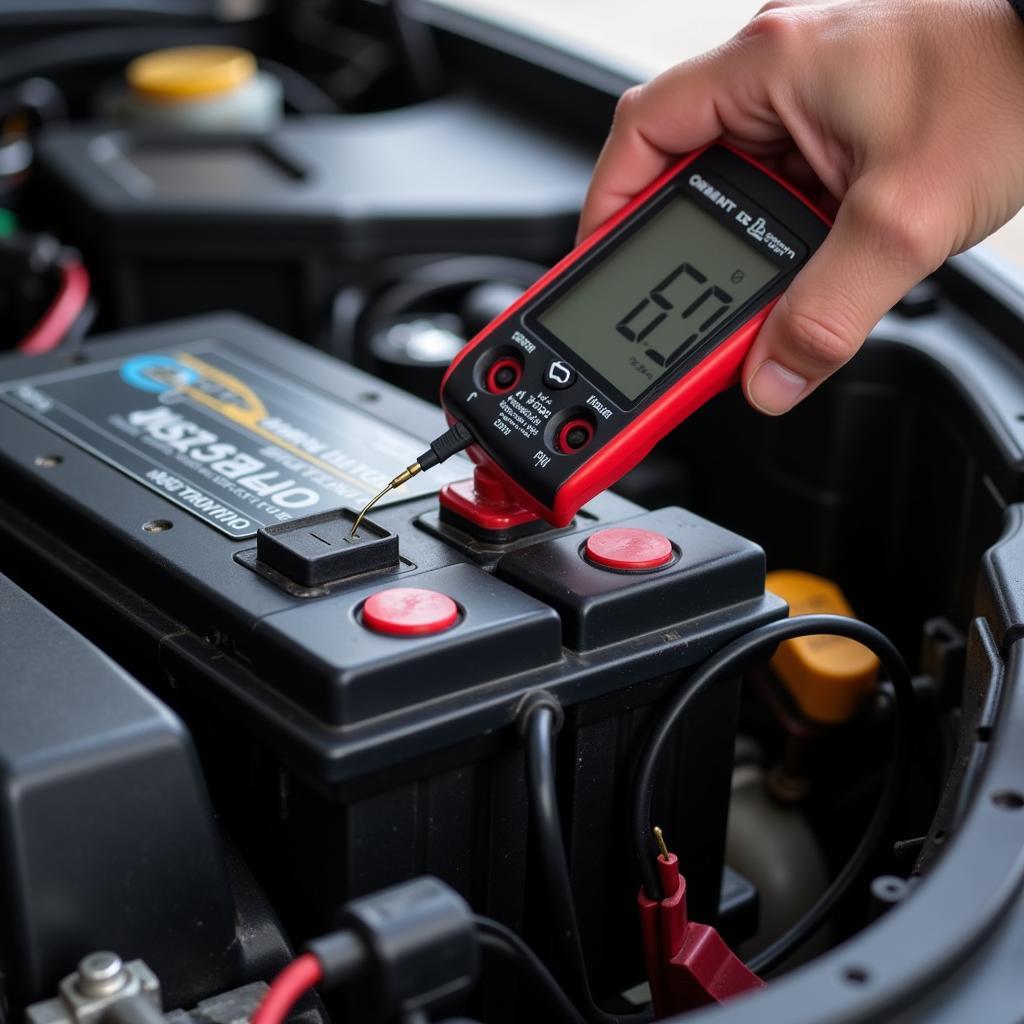 Car Battery Check
Car Battery Check
 Car Starter Motor Check
Car Starter Motor Check
FAQs
Q: How long does it take for a car battery to die completely?
A: A car battery can take anywhere from a few hours to several days to die completely, depending on the battery’s age, condition, and the amount of electrical drain on the system.
Q: What are some common signs that my car battery is dying?
A: Common signs include dim headlights, slow cranking, clicking sounds when starting, and the car stalling unexpectedly.
Q: What is the best way to jump-start a car battery?
A: Ensure the vehicles are parked on a level surface and the handbrakes are engaged. Connect the positive (red) cable to the positive terminal of the dead battery, then to the positive terminal of the good battery. Connect the negative (black) cable to the negative terminal of the good battery, then to a metal grounding point on the frame of the dead car. Start the good car and allow it to charge the dead battery for a few minutes before attempting to start the dead car.
Q: How often should I replace my car’s spark plugs?
A: The recommended replacement interval for spark plugs varies depending on the vehicle and driving conditions. However, a general guideline is to replace them every 30,000-50,000 miles.
Q: How do I know if my fuel filter needs to be replaced?
A: A clogged fuel filter can cause reduced fuel flow, leading to sluggish acceleration, poor fuel economy, and even engine stalling. If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s best to replace the fuel filter.
Q: What is a vacuum leak, and how can I fix it?
A: A vacuum leak is a hole or crack in the air intake system, which allows unfiltered air to enter the engine. This can disrupt the air-fuel mixture, causing engine problems. To fix it, locate the leak and seal it with an appropriate sealant or replace the damaged part.
Common Situations and Troubleshooting
Car won’t crank at all: Check battery connections, battery health, and starter motor functionality.
Car cranks but won’t start: Inspect spark plugs, ignition coil, fuel pump, fuel filter, and air filter.
Car starts but dies immediately: Check fuel injectors, air intake for leaks, and ignition timing.
Need Help?
If you’re still unsure about the cause of your car’s starting issue, don’t hesitate to seek professional assistance. Our team of certified mechanics is here to help. Contact us at WhatsApp: +1(641)206-8880, Email: [email protected], or visit us at 276 Reock St, City of Orange, NJ 07050, United States. We’re available 24/7 to provide you with expert advice and solutions to keep your car running smoothly.