A car alternator plays a crucial role in your vehicle’s electrical system, and understanding common alternator problems can save you time, money, and potential headaches on the road. This article delves into the ins and outs of car alternator issues, equipping you with the knowledge to identify, troubleshoot, and resolve them.
 Car Alternator Diagram
Car Alternator Diagram
What Does a Car Alternator Do?
The alternator functions as the heart of your car’s electrical system, generating the power needed to run everything from your headlights and radio to essential components like the engine control unit and fuel pump. Unlike a traditional battery, which stores electrical energy, the alternator constantly produces electricity while the engine is running.
Here’s a simplified breakdown of the alternator’s role:
- Engine Starts: When you start your car, the battery provides the initial power.
- Alternator Takes Over: Once the engine is running, the alternator kicks in to power the electrical system and recharge the battery, replenishing the energy used during startup.
- Continuous Power Supply: As long as your engine is running, the alternator ensures a steady supply of electricity, keeping your car running smoothly and preventing the battery from draining.
Common Car Alternator Problems
Identifying alternator problems early can prevent unexpected breakdowns and costly repairs. Here are some common signs of a failing alternator:
1. Dimming or Flickering Lights
One of the first noticeable symptoms of alternator issues is dimming or flickering lights. This fluctuation occurs because the alternator struggles to produce enough power to keep up with the electrical demands of your vehicle, especially when multiple components are in use simultaneously.
2. Warning Light on Dashboard
Most modern vehicles feature a dedicated battery or charging system warning light on the dashboard. When illuminated, this light usually resembles a battery icon or contains the letters “ALT” or “GEN,” indicating a problem with the charging system, often related to the alternator.
3. Dead Battery
A dead battery can be a telltale sign of a failing alternator. If your car doesn’t start and requires jump-starting frequently, the alternator might not be recharging the battery properly, leading to a complete loss of charge over time.
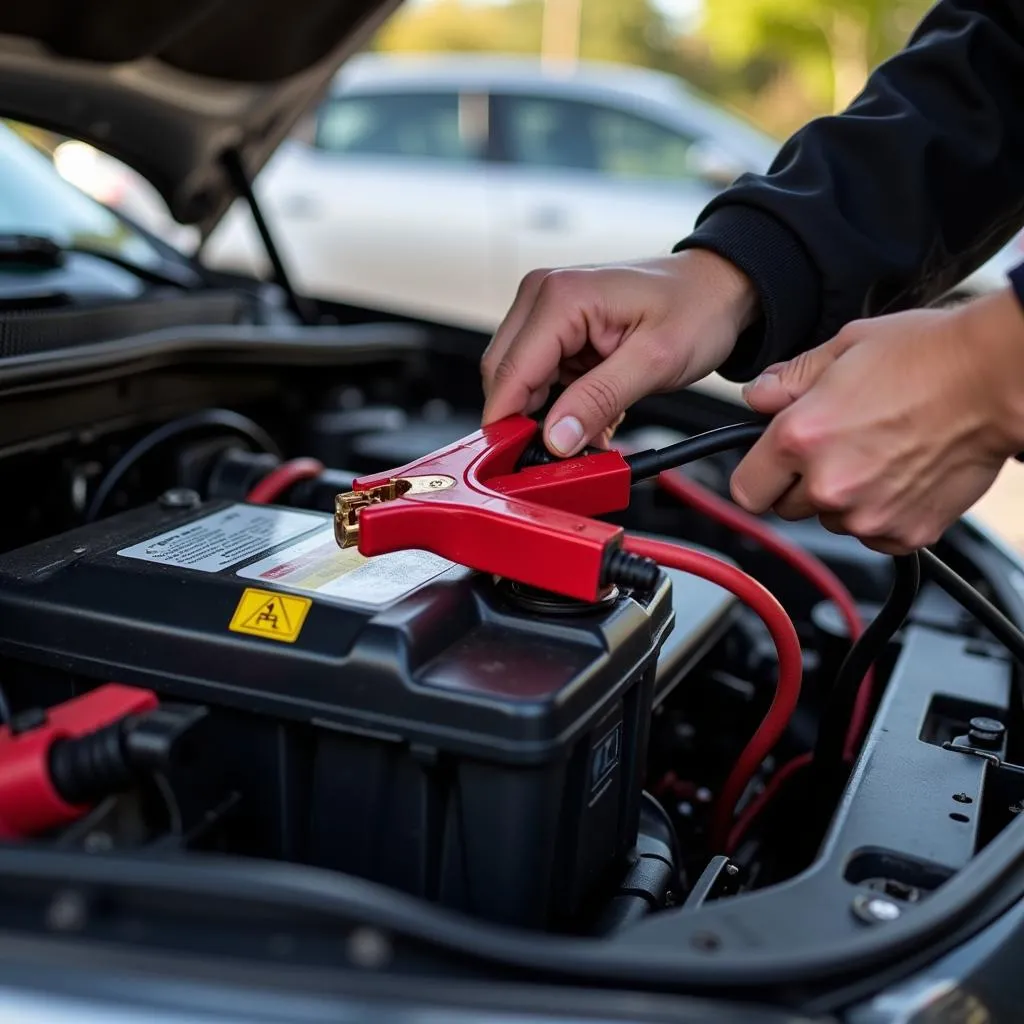 Jump Starting a Car Battery
Jump Starting a Car Battery
4. Whining or Growling Noises
Worn-out bearings within the alternator can produce a distinctive whining or growling sound, especially when the engine is idling or under load. This noise often indicates mechanical wear and tear within the alternator, requiring immediate attention to prevent further damage.
5. Difficulty Starting the Engine
If your car struggles to start, cranking slowly or requiring multiple attempts, a failing alternator could be the culprit. The alternator provides the initial surge of power needed for ignition, and a weakened alternator might not deliver sufficient energy for a smooth start.
What Causes an Alternator to Go Bad?
Understanding the causes of alternator failure can help you take preventive measures and prolong the lifespan of this essential component. Here are some key factors that contribute to alternator problems:
- Worn-out Brushes: The brushes inside the alternator transmit electrical current to the rotor. Over time, these brushes can wear down, reducing their effectiveness and leading to decreased alternator output.
- Damaged Voltage Regulator: The voltage regulator maintains a constant voltage output from the alternator. A faulty voltage regulator can cause overcharging or undercharging of the battery, potentially damaging both the battery and other electrical components.
- Worn-out Bearings: As mentioned earlier, worn-out bearings create friction, leading to noise and reduced alternator efficiency. Extreme wear can eventually cause the alternator to seize completely.
- Fluid Leaks: Leaks from engine oil or power steering fluid can contaminate the alternator, damaging its internal components and shortening its lifespan.
- Excessive Electrical Load: Continuously running power-hungry accessories like high-powered audio systems, aftermarket lighting, or additional electronics can put a strain on the alternator, leading to premature wear and tear.
How to Test a Car Alternator
Testing your car’s alternator is crucial for confirming if it’s the source of electrical problems. While it’s best to consult a qualified mechanic for a thorough diagnosis, you can perform a basic alternator test at home using a multimeter:
- Safety First: Disconnect the negative battery cable before starting any electrical testing.
- Connect Multimeter: Set your multimeter to the DC voltage setting and connect the red probe to the positive battery terminal and the black probe to the negative terminal.
- Check Battery Voltage: With the engine off, the multimeter should read around 12.6 volts, indicating a healthy battery charge.
- Start the Engine: Start your car and observe the multimeter reading. The voltage should increase to around 13.5 to 14.5 volts, signifying that the alternator is charging the battery.
- Check Under Load: Turn on electrical components like headlights, the radio, and the blower fan. The voltage should remain within the 13.5 to 14.5-volt range. A significant drop in voltage indicates a potential alternator problem.
How Much Does It Cost to Fix an Alternator?
The cost of alternator repair or replacement can vary depending on several factors, including the make and model of your vehicle, the severity of the problem, labor costs in your area, and whether you choose to go with a new or remanufactured alternator. On average, you can expect to pay between $300 and $800 for alternator replacement, including parts and labor.
 Mechanic Replacing Car Alternator
Mechanic Replacing Car Alternator
How to Prevent Car Alternator Problems
Taking proactive steps to maintain your car’s electrical system can significantly reduce the risk of alternator failure:
- Regular Inspections: Have your alternator inspected by a qualified mechanic during routine maintenance checks.
- Battery Care: Maintain your car battery properly, as a failing battery can put extra strain on the alternator.
- Manage Electrical Load: Avoid excessive use of power-hungry accessories, especially when the engine is idling.
- Address Fluid Leaks: Promptly fix any fluid leaks that could potentially damage the alternator.
Conclusion
Understanding car alternator problems empowers you to address electrical issues effectively and keep your vehicle running smoothly. By recognizing the signs of alternator failure, performing basic troubleshooting, and following preventive maintenance tips, you can avoid unexpected breakdowns and extend the lifespan of this vital component.
Remember, when in doubt, always consult a trusted mechanic for a professional diagnosis and repair.