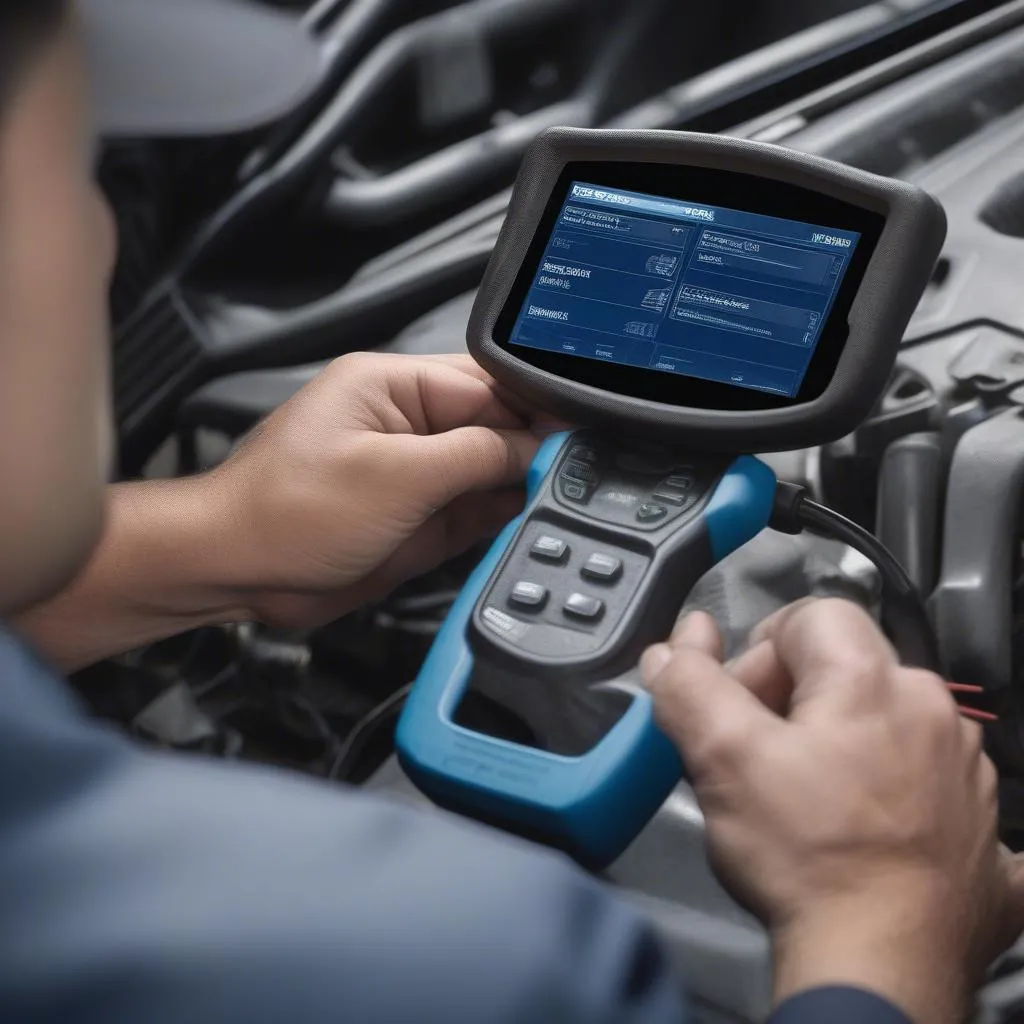
Imagine this: you’re cruising down the Pacific Coast Highway in your sleek Audi A4, California sun warming your face. Suddenly, your check engine light pops on. A quick stop at a garage in Malibu, and the mechanic mumbles something about a “bad cat.” A wave of dread washes over you. Could it be the dreaded (and expensive) catalytic converter?
Before you panic, remember knowledge is power. Knowing how to diagnose a faulty catalytic converter, even with a simple scan tool, can save you time, money, and unnecessary headaches.
Decoding the “Bad Cat”: What Does It Mean?
Before we dive into the world of scan tools, let’s understand what a “bad cat” actually means.
From a mechanic’s perspective, a “bad cat” usually refers to a failing or clogged catalytic converter. This essential emissions control device, often located beneath your car, converts harmful exhaust gases into less harmful substances before releasing them into the atmosphere.
Technically speaking, a failing catalytic converter struggles to efficiently convert these gases. This can trigger your check engine light and lead to decreased engine performance, reduced fuel economy, and even that dreaded rotten egg smell from your exhaust.
But don’t worry, understanding the signs and using a scan tool can help you identify the issue early on.
Unmasking the Culprit: Using a Scan Tool to Diagnose a Bad Cat
Now, let’s talk about how to use a scan tool to confirm your suspicions about a faulty catalytic converter. While a scan tool won’t directly tell you “your cat is bad,” it can provide crucial clues.
Here’s what to look for:
1. Check Engine Light and Oxygen Sensor Codes:
- A flashing check engine light often signals a serious issue, potentially a failing catalytic converter.
- Connect your scan tool and look for oxygen sensor codes, particularly those related to the sensors located before and after the catalytic converter (Bank 1 Sensor 1, Bank 1 Sensor 2, etc.).
- Example: Let’s say you’re working on a 2018 Ford F-150 and the scan tool shows code P0420 (“Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold Bank 1”). This strongly indicates a problem with the catalytic converter on engine bank 1.
2. Comparing Oxygen Sensor Readings:
- The scan tool will display live data from your oxygen sensors.
- A healthy catalytic converter should show a fluctuating signal from the upstream (pre-cat) oxygen sensor and a relatively steady signal from the downstream (post-cat) oxygen sensor.
- Red Flag: If both oxygen sensors show similar, fluctuating readings, it suggests the catalytic converter isn’t doing its job of converting the exhaust gases properly.
3. Examining Fuel Trim Values:
- Your car’s computer (ECU) constantly adjusts the fuel-air mixture to optimize performance and emissions.
- High positive fuel trim values can indicate a rich fuel mixture, often a symptom of a clogged catalytic converter.
Expert Insight: Renowned automotive engineer, Dr. Emily Carter, author of “Advanced Automotive Diagnostics,” suggests, “While scan tools are powerful tools, always remember they provide data points, not definitive diagnoses. Combining scan tool data with a thorough visual inspection and other tests is crucial.”
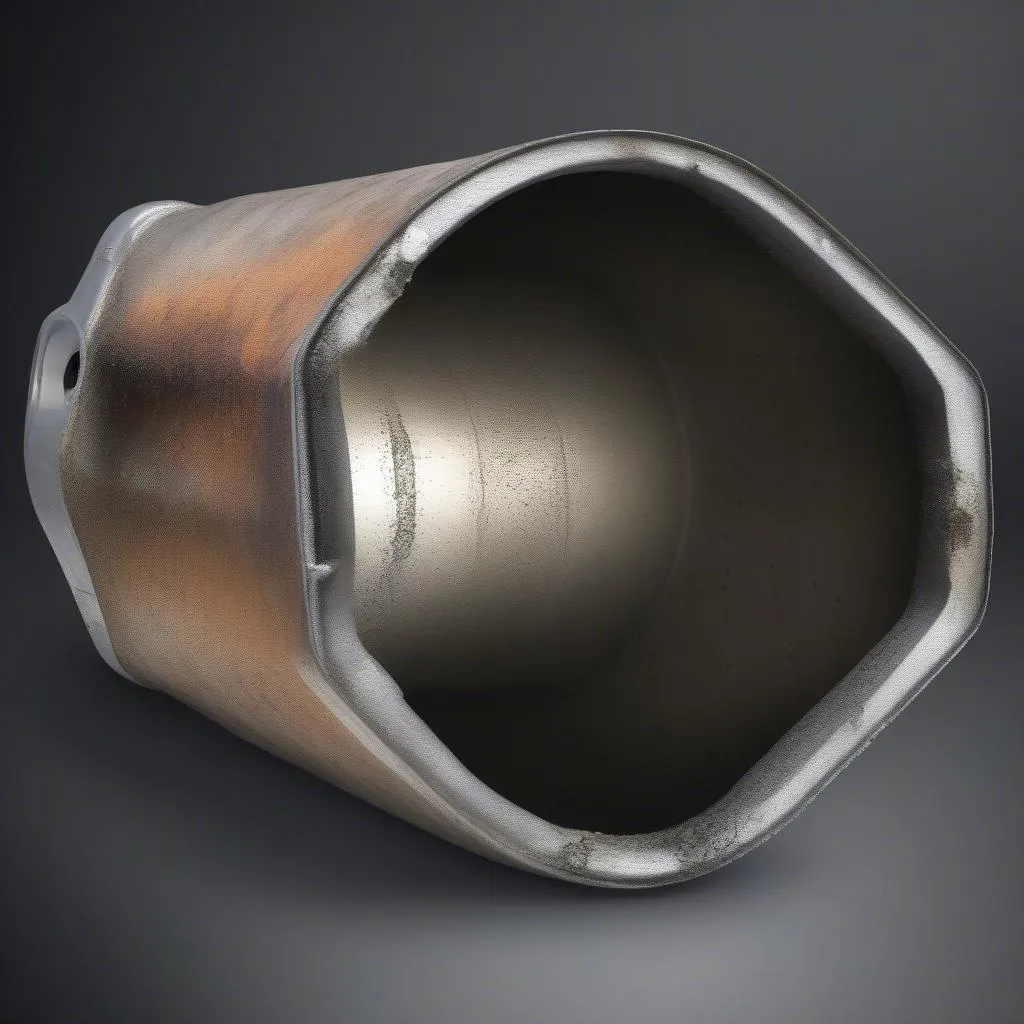 damaged catalytic converter
damaged catalytic converter
Beyond the Scan Tool: Other Telltale Signs
While a scan tool can provide valuable insights, don’t underestimate the power of observation.
- Rattling Noise: A rattling sound coming from beneath your car, especially when accelerating, could indicate a damaged catalytic converter core.
- Loss of Power: A clogged catalytic converter can restrict exhaust flow, leading to decreased engine power and sluggish acceleration.
- Failed Emissions Test: If your vehicle fails an emissions test, a faulty catalytic converter is often the culprit.
What if My Scan Tool Shows No Codes?
It’s possible to have a failing catalytic converter even if your scan tool doesn’t display any specific codes. Remember, scan tools aren’t foolproof. If you suspect a problem, consider these steps:
- Visual Inspection: Look for signs of physical damage, discoloration, or melting on the catalytic converter.
- Exhaust Back Pressure Test: This test, often performed by a mechanic, measures the pressure in the exhaust system and can help identify a restriction caused by a clogged catalytic converter.
- Consult a Professional: When in doubt, seek the expertise of a qualified mechanic specializing in automotive diagnostics.
Frequently Asked Questions:
Q: Can I drive with a bad catalytic converter?
A: While technically possible for short distances, driving with a bad catalytic converter is not recommended. It can further damage your vehicle, decrease fuel efficiency, and increase harmful emissions.
Q: How much does it cost to replace a catalytic converter?
A: The cost varies depending on your car’s make and model. However, expect a significant investment, often ranging from several hundred to over a thousand dollars.
Q: Can I prevent my catalytic converter from failing?
A: Regular vehicle maintenance, including timely oil changes and addressing engine issues promptly, can help extend the life of your catalytic converter.
Need More Help with Car Diagnostics?
Diagnosing car problems can be challenging, but you don’t have to go it alone! For expert assistance with scan tools, diagnostic software, and any automotive issue, don’t hesitate to contact us via WhatsApp at +84767531508. Our team of experienced mechanics is available 24/7 to provide personalized guidance and support.
 auto mechanic using scan tool
auto mechanic using scan tool
Keep Your Engine Purring: Knowledge is Key
Remember, understanding how to use a scan tool and recognizing the signs of a bad catalytic converter can save you from costly repairs and unnecessary stress. For more insightful articles on car maintenance, diagnostics, and repair, explore our website Diag XCar. We’re here to empower you with the knowledge to keep your car running smoothly for miles to come.